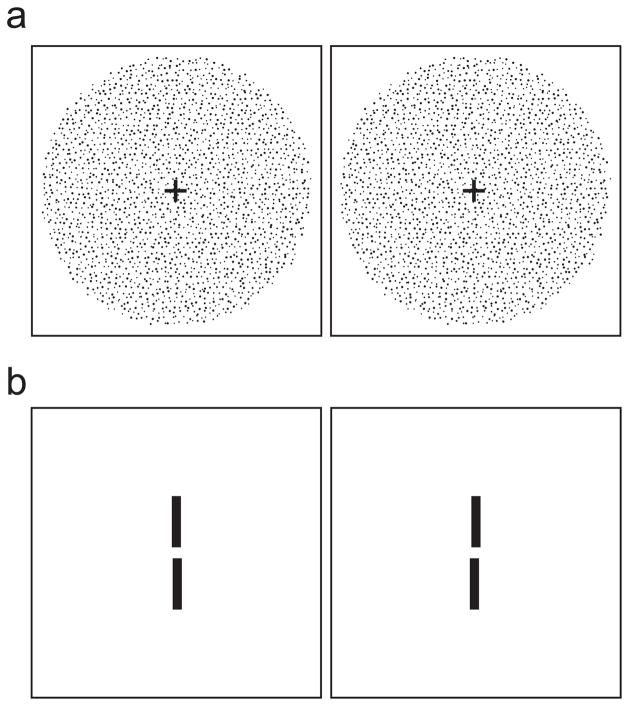
Figure 1.
Stereo stimuli. a) Random-dot stereogram depicting sinusoidal depth corrugation. Cross-fuse (direct left eye to right image and right eye to left) and you should see a corrugation oriented 10° from horizontal. In the experiment, the stimuli were white dots on a dark background. b) Two-line stereogram. The reference line was presented with zero disparity (i.e., in the plane of the fixation target which is not shown). The test line was below the reference line and had either crossed or uncrossed disparity. Cross-fuse the stimulus and you should see that the test line is slightly farther than the reference line. In the experiment, the stimuli were white lines on a dark background.