Fig. 7.
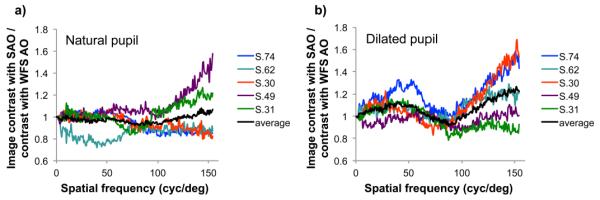
Ratio of the image contrast for averaged retinal images acquired with the sensorless control method to those acquired with traditional wavefront sensor based control in 5 subjects when imaging through a. natural and b. dilated pupils. Dilated pupil size was 8 mm, undilated pupil size was approximately: S.30, 6 mm; S.31, 4 mm; S.49, 6 mm; S.62, 4 mm; S.74, 6 mm. Contrast ratios were calculated by taking the square root of the ratio of the normalized image power spectra. With natural pupils the contrast ratio averaged across subjects (black line) is not significantly different from 1, indicating that sensorless control yielded images of comparable contrast to those obtained with wavefront sensor based control. However when imaging through dilated pupils the contrast ratio averaged across subjects was greater than 1 at most spatial frequencies, indicating higher contrast with sensorless control. The average contrast improvement with sensorless control approached 25% at the highest spatial frequencies.
