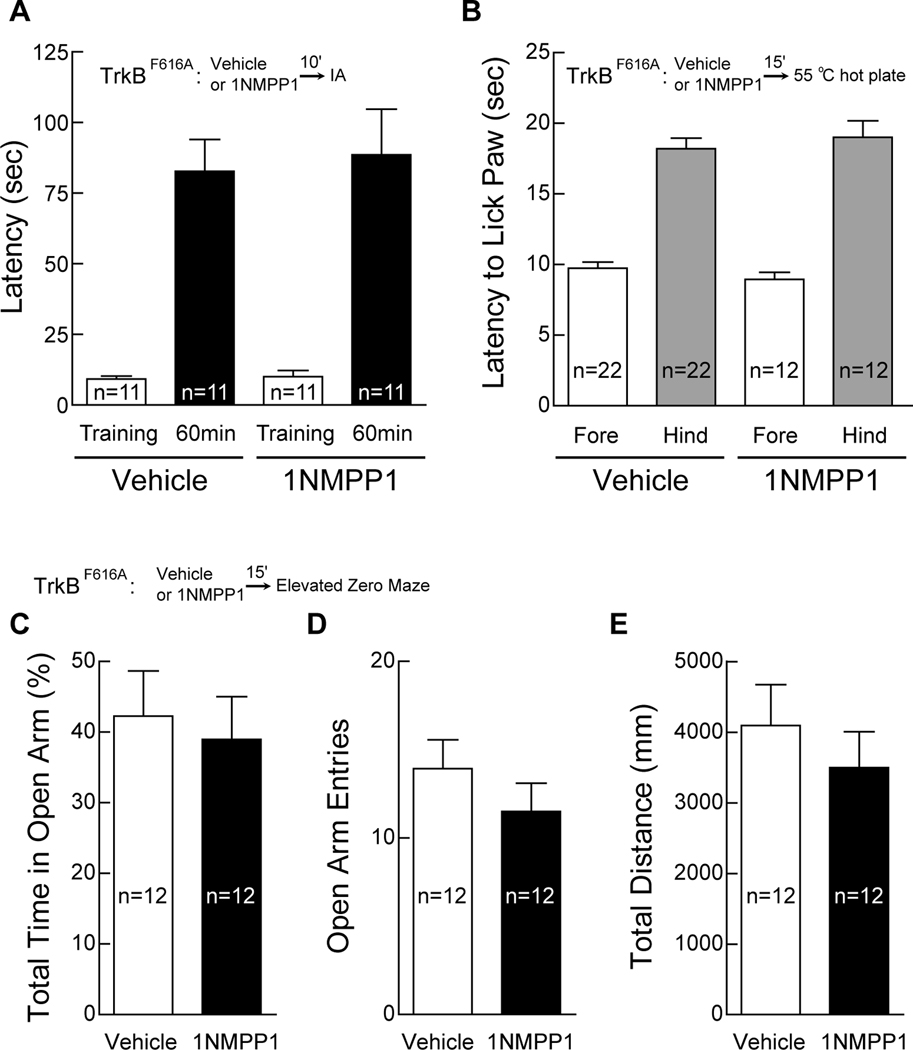
Figure 8. Normal short-term memory, pain sensory, emotional state and locomotion after TrkB inhibition by 1NMPP1.
(A) Normal short-term memory after TrkB inhibition by 1NMPP1. At 10 min after IP-injection with 1NMPP1 or vehicle, mice were trained in an inhibitory avoidance (IA) task with 2 weak foot shocks (0.1 mA, 100 ms) at 1 sec interval. Latency to step through the door from illuminated chamber to dark chamber was recorded as measurement of memory and plotted as mean ± s.e.m.
(B) Normal pain sensory after TrkB inhibition by 1NMPP1. Hot plate test was performed at 55°C. Latency to lick fore paw and hind paw was plotted as mean ± s.e.m.
(C–E) Normal emotional state and locomotion after TrkB inhibition by 1NMPP1. Elevated zero maze tests were performed using the ring-shaped platform consisting of two walled (white Plexiglas) sections separated by open sections of equal length. Activity of each mouse was recorded for five minutes. Mice injected with 1NMPP1 spent similar amount of time in open arms as compared with those injected with vehicle (C). In addition, 1NMPP1 did not affect the number of times that mice entered the open arms (D) and the total distance that mice traveled in the maze (E).