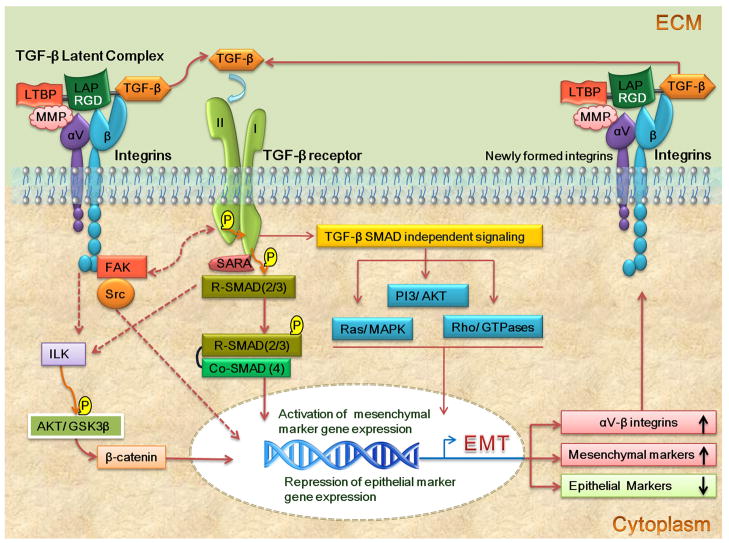
Figure 2.
αV integrins recognize a RGD motif present in the LAP of TGF-β. This binding induces either adhesion-mediated cell forces and/or brings latent TGF-β into the proximity of MMPs which consequently lead to the liberation/activation of the TGF-β homodimer from its latent complex. Upon activation, the TGF-β homodimer will bind to the Type II TGF-β receptor initiating TGF-β-Smad signaling which upregulates the expression of αV integrins in addition to that of other EMT markers. These newly formed integrins can liberate more TGF-β from its latent complex, sustaining and reinforcing TGF-β induced EMT progression. This cooperative feed forward loop between αV integrins and TGF-β can lead to the unregulated TGF-β signaling responsible for a number of TGF-β-associated disorders.