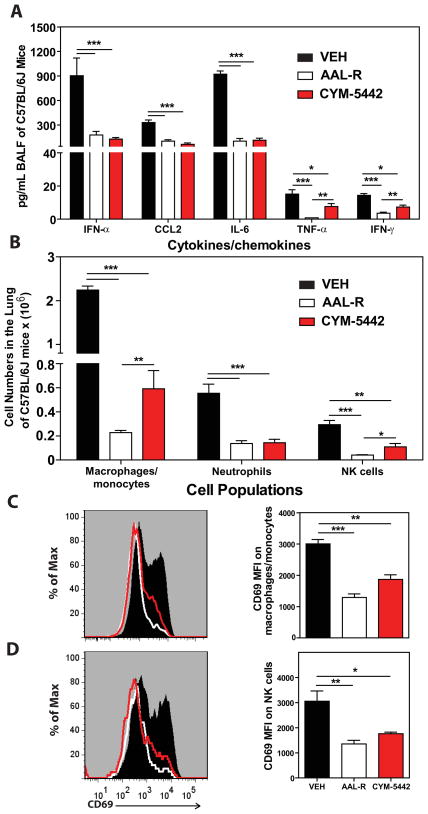
Figure 1.
S1P1 receptor agonism suppresses early pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine production and innate immune cell recruitment during influenza virus infection. Mice were infected with 1 × 104 PFU WSN influenza virus and either Vehicle (water), AAL-R (0.2mg/kg) (1 hour post-infection) or CYM5442 (2mg/kg) (1,13, 25 and 37 hours-post-infection) were administered i.t. to mice. (A) Pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines were measured 48 hours post-infection in BALF by ELISA. (B) Total numbers of innate immune cells were quantified from collagenase digested lungs by flow cytometry at 48 hours post-influenza virus infection. (C) Histograms (left) and mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) (right) of CD69 expression on macrophages was quantified on vehicle, AAL-R or CYM-5442 treated mice 48 hours post-influenza virus infection by flow cytometry staining. (D) Histograms (left) and MFI (right) of NK cell CD69 expression quantified as done in C. Data represent average ± SEM from 4–5 mice/group. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005. Results are representative of greater than 6 independent experiments.