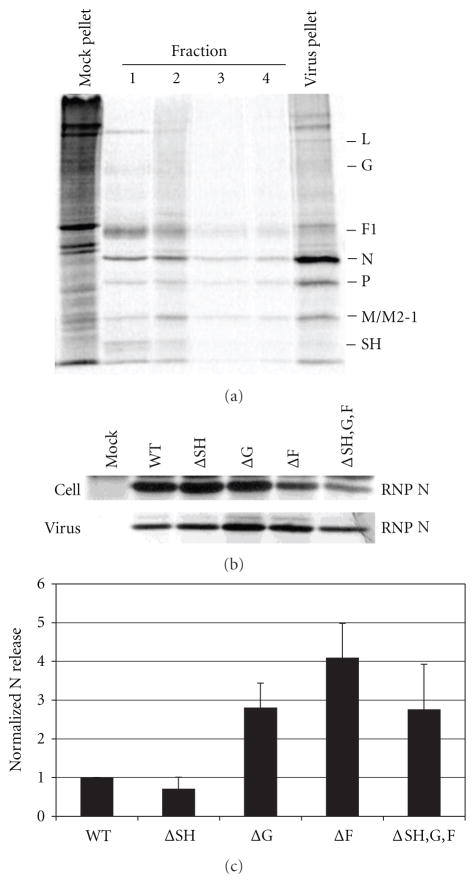
Figure 5.
Effect of glycoprotein deletions on the release of virions from infected A549 cells. A549 cells were infected with WT or glycoprotein deleted virus and particles released into the supernatant were quantified as a percent of total virus produced. The N protein in isolated RNPs was used to quantitate the virus in cell lysates and in virions. (a) Separation of RNPs containing the viral genome and associated proteins from soluble proteins in infected cell lysates. Infected cell lysates were ultracentrifuged through a 40% glycerol cushion. Fractions were taken from the top of the tube (fraction 1) to the bottom of the tube (fraction 4) in 0.5 mL volumes. The pellet was resuspended in 0.1 mL lysis buffer. Viral proteins in each fraction and the pellet were immunoprecipitated and analyzed on a 12% SDS polyacrylamide gel. A representative gel is shown. HRSV proteins are indicated on the right of the gel. (b) Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) associated N protein in infected cell lysates was harvested as described above and in Section 4, and viral proteins were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and electrophoresis on 12% SDS gels. Released virions were recovered from supernatant fluids by centrifugation and viral proteins were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and electrophoresis on 12% SDS gels. A representative gel is shown. (c) Bar graph depicts the percent of N protein quantified in released virus from total RNP-associated N protein quantified in infected cell lysate and in released virus. The N protein was quantitated by phosphoimage analysis. Error bars represent standard deviation from at least three experiments.