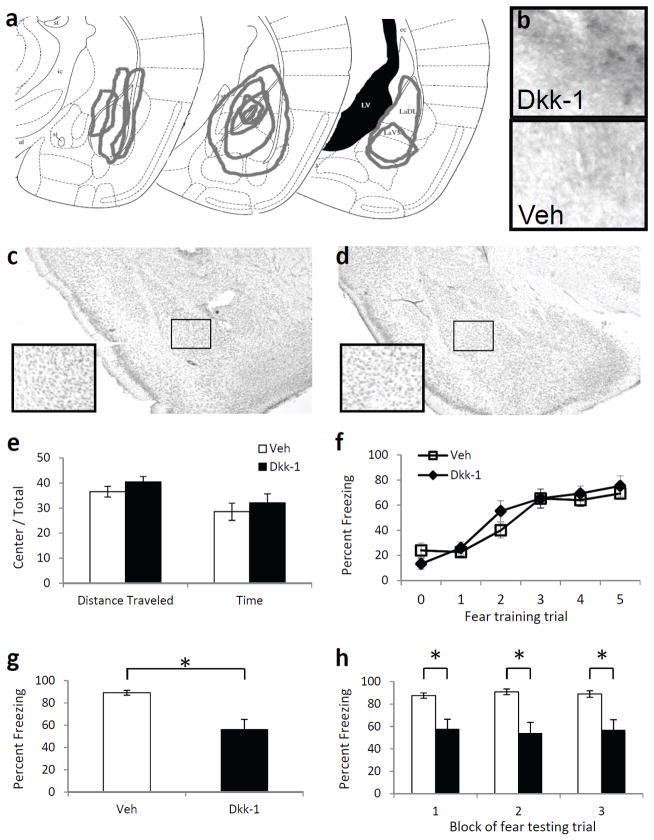
Figure 3. The effect of Dkk-1 in the amygdala on fear learning and memory.
(a) Schematic diagram, based on Paxinos & Franklin (2001), illustrating the extent of infusions across animals via stereotaxic cannulae into the amygdala based on immunohistochemistry. (b) 10× light microscopy of basolateral amygdala regions following immunohistochemical analyses of Dkk-1 in animals receiving bilateral amygdala injections of either Dkk-1 or vehicle. (c,d) Cresyl violet staining of sections showing the absence of damage in Dkk-1 (c) or vehicle (d) infected regions. (e) Activity measures of mice receiving injections of vehicle or Dkk-1 and placed in an open field apparatus for 10 m. (f) Acquisition curve showing percent time spent freezing during each tone prior to footshock presentation. (g) Percent time spent freezing when tested 48 h after fear conditioning, and presented with 15 tone presentations. (h) Freezing data from (g), presented in 3 blocks of 5 tone presentations. n = 10 per group. Mean ± s.e.m. * P < 0.01, significant differences (two-tailed t-tests).