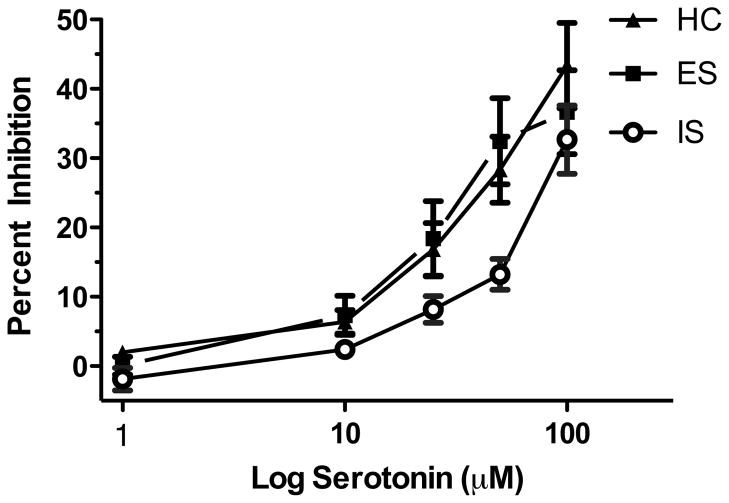
Figure 3.
Inescapable stress (IS) selectively impairs serotonin-mediated inhibition of dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) cell firing 24 hr following stress treatment. The graph depicts the effect of stress treatment on serotonin-mediated inhibition of DRN cell firing. Groups are designated as the following: homecage control (HC), closed triangles; escapable stress (ES), closed squares; IS open circles. Data are expressed as mean percent inhibition ± SEM. Mean percent inhibition of DRN cell firing was significantly different in IS, compared to ES and HC (p < 0.05).