Figure 6. CRF1 mediates stress-induced pathological tau inclusions, neurodegeneration and fear-associated learning.
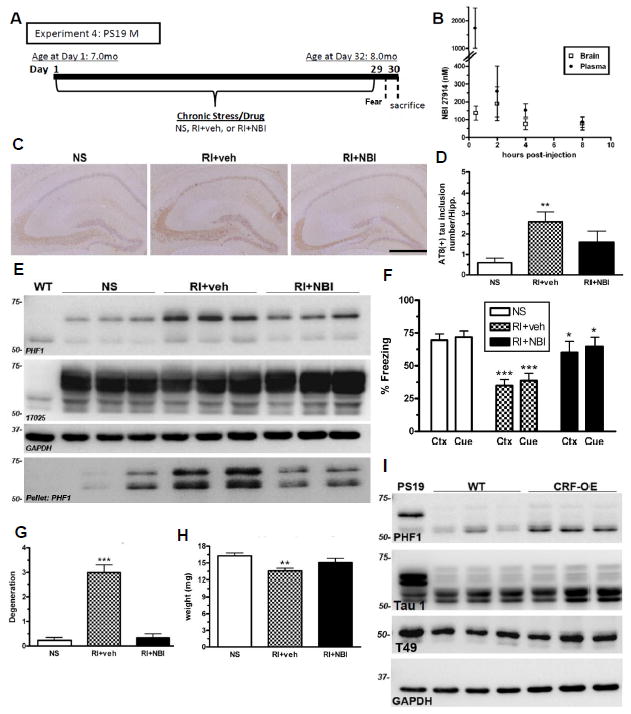
(A) Experimental design of Experiment 4; male PS19 mice were exposed to NS or RI stress with pre-stress CRF1 antagonist (NBI) or vehicle subcutaneous injections (n=8/group). (B) A small pilot utilizing adult WT female mice (n=3/group) was conducted to measure brain and plasma levels of NBI after a 10mg/kg sc injection. (C) Representative pictomicrographs demonstrate that vehicle-treated RI mice displayed significantly higher AT8 (+) tau inclusions in the hippocampus, quantified in (D) (F(2,25)=7.15, p=0.05), as well as soluble and insoluble PHF1, but not 17025 levels by western blot (E) that was blocked by a pre-stress injection of NBI. (F) Vehicle-treated RI mice also displayed fear-related learning impairments in both context (F(2,28)=12.4, p<0.05) and cued (F(2,28)=9.3, p<0.05) fear conditioning which was significantly prevented by NBI. Data show mean % freezing ± SEM. (G) Compared to NS, vehicle-treated mice had significantly lower hippocampal weight (F(2,44)=6.44, p=0.004) and significantly increased NeuN-IR (+) degeneration scores (F(2,28)=6.19, p<0.001) (H) while NBI treatment significantly prevented both effects. (I) Lastly, phosphorylated tau was quantified in the hippocampus of 10 mo old CRF-OE mice and WT littermate controls. A substantial elevation was observed in PHF1 levels in CRF-OE compared to WT littermates without a change in Tau 1 and T49 level. Data show mean PHF1 score ± SEM. Scale bar = 0.5mm. p***<0.001, p**<0.01, from NS. p*<0.05, from RI+veh.
