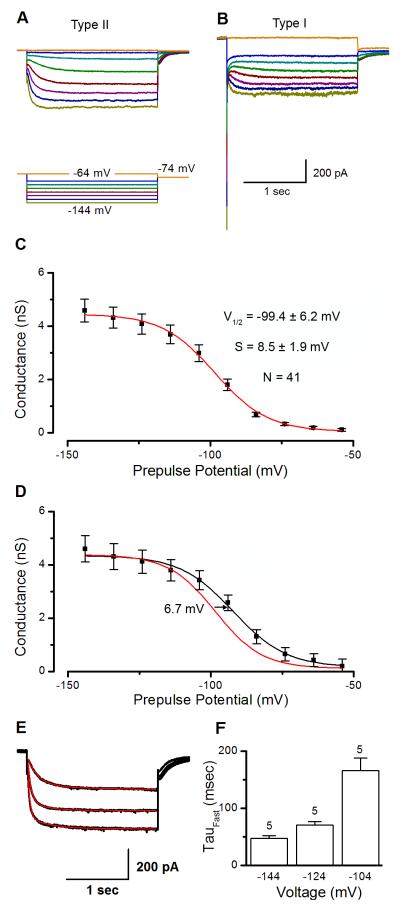
Figure 2.
Ih in wild-type vestibular hair cells. Representative traces showing voltage-dependent currents through HCN channels in P8-10 mouse utricular hair cells. Currents were evoked with voltage steps between −144 mV and −64 mV from a resting potential of −64 mV using the protocol shown below panel A. A, B, Representative wild-type currents measured from a type II (A) and type I (B) hair cell. Note the large, slowly activating inward current typical of Ih. In panel B, IK,L active at rest is evident as a standing outward current and the large, fast inward current that deactivates at negative potentials. C, Activation curve generated from 41 type II hair cells. Tail currents were measured at −74 mV to eliminate contamination from IK1 and converted to conductance by dividing by driving force (30 mV). The data were fitted with a Boltzmann function (red line). D, Activation curve generated from 9 type II hair cells in the presence of 200μM 8-Br-cAMP. Data were fitted with a Boltzmann function (black line). The Boltzmann curve from Figure 2C is replotted to facilitate comparison. E, Current evoked by steps to −144, −124, and −104 mV in a type II hair cell. Current amplitudes were normalized to facilitate comparison of activation kinetics. Red lines are double exponential fits of the currents. Currents were measured in the presence of Ba2+ in order to minimize the effect of the fast inward rectifier, IK1. Mean fast time constants of activation for five cells are shown in F.