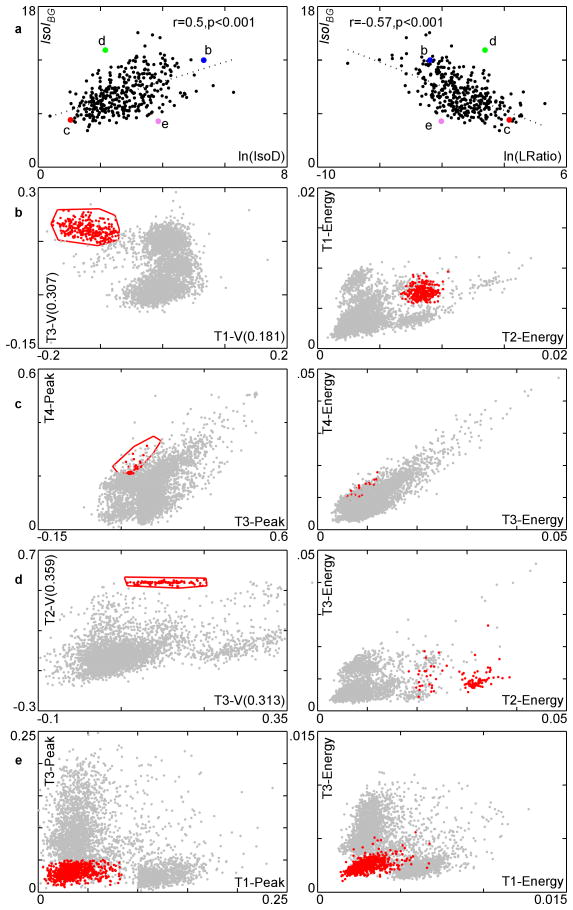
Figure 4.
Comparison of IsoIBG with ln(IsoD), ln(LRatio) on all clusters in the 350 cluster dataset along with several case studies. a. Plot of IsoIBG vs. ln(IsoD) and ln(LRatio). Larger, labeled points represent clusters discussed in text. These clusters are shown in parts b-e. In b-e, the red cluster is the cluster of interest (highlighted point from part a) and the blue cluster is its nearest neighbor. The gray points are the remaining spikes. The left column of b-e shows the slices of the feature space used by IsoIBG, and the right column shows slices of the feature space used by IsoD. Voltage in units of mV. b. A well-isolated cluster according to both measures. c. A poorly-isolated cluster according to both measures. d. A well-isolated cluster according to IsoIBG, poorly-isolated cluster according to IsoD/LRatio. e. Poorly-isolated cluster according to IsoIBG, well-isolated cluster according to IsoD/LRatio.