Figure 7. Subtype dependent bimodal response to semaphorins is distinguished by protein synthesis requirement.
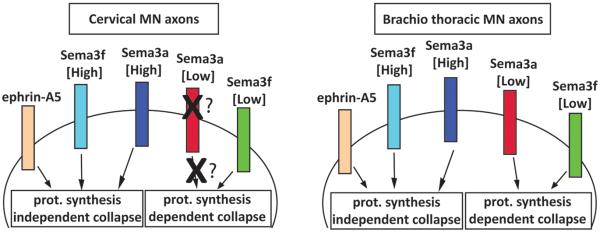
Protein synthesis dependent and independent pathways are activated by different concentration of Sema3f in both cervical and brachio-thoracic motor neurons. In contrast the “low” protein synthesis dependent Sema3a pathway is observed only in brachio-thoracic motor neurons while both populations of neurons are responsive to high Sema3a (in a protein synthesis independent manner). The cervical motor neurons appear to lack the receptors or the components of the transduction cascade linking low concentration of Sema3a to the protein translation machinery. Collapse induced by Ephrin-As at all tested concentrations is independent of the protein synthesis pathway.
