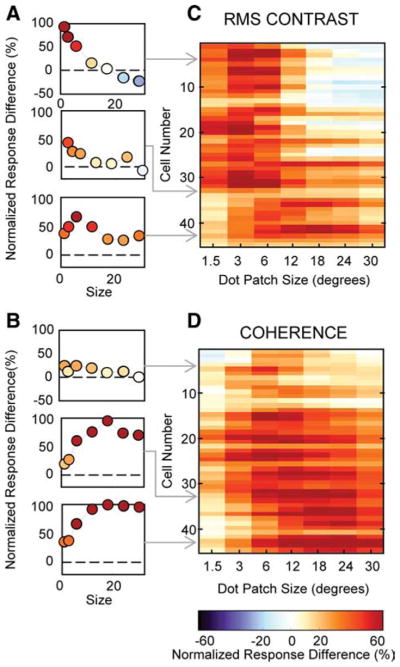
Figure 4.
Differences in firing rates between high and low conditions for contrast and coherence in MT. A, Difference curves resulting from subtracting low from high contrast curves, normalized to the maximum firing rate. Positive values indicate larger responses at high contrast, and negative values indicate larger responses at low contrast. B, Analogous difference curves for coherence size tuning. C, Contrast difference tuning curves for every neuron in the population, ordered by high coherence suppression index. The blue regions represent increased responses in the low condition, white represents similar responses, and orange represents decreased responses. Population plots were smoothed with a Gaussian (1 pixel SD) to highlight trends in the population data. D, Coherence difference curves for every neuron in the population, ordered by high coherence suppression index.