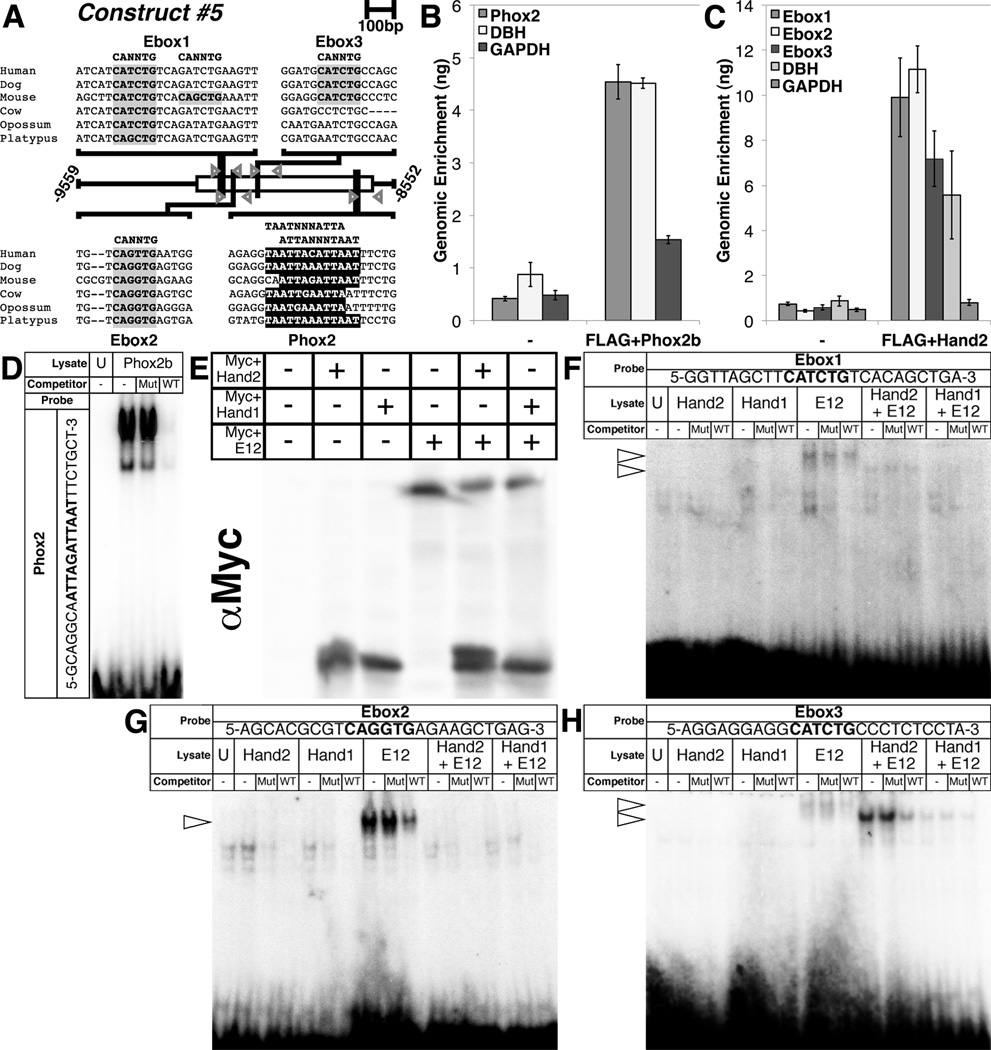
Figure 3. Phox2b and Hand2 bind to evolutionarily conserved consensus sites within the minimal Hand1 SN enhancer.
(A) A schematic shows three conserved E-box binding sites (highlighted in gray)and one conserved Phox2 binding site (highlighted in black) in the 1007bp minimal Hand1 SN enhancer contained in Construct #5. Grey arrowheads denote ChIP primers flanking each of these binding sites. B, C) Immunoprecipitation of either FLAG+Phox2b or FLAG+Hand2 cross-linked complexes using α-FLAG antibody, produces enrichment of the Phox2 site-containing region (B) and three E-box-containing regions (C),respectively, in a manner similar to that of a positive control (DBH), but not a negative control (GAPDH). Error bars represent standard error. D) EMSA using lysate programmed with FLAG+Phox2b demonstrate binding to a radiolabeled oligonucleotide mimicking the Phox2 consensus site in the Hand1 SG enhancer. E) A Western blot for α-Myc verifies that Myc+Hand2 and Myc+Hand1 transcribed in vitro either in the presence or absence of Myc+E12 were synthesized in equivalent amounts. F – H) EMSAs employing these lysates reveal that E-box1 (F) is weakly bound by E12 homodimers and Hand2–E12 heterodimers, but not Hand1–E12 heterodimers, nor Hand2 or Hand1 homodimers, that E-box2 (G) is bound solely by E12 homodimers, and that E-box3 (H) is not bound by Hand2 or Hand1 homodimers, is weakly bound by E12 homodimers and Hand1–E12 heterodimers, and is robustly bound by Hand2–E12 heterodimers. Binding in all EMSAs was competitively inhibited by unlabeled wild-type (WT) oligos, but not by unlabeled mutant (Mut) oligos. For all EMSAs, unprogrammed lysate (U) is used to control for non-specific protein binding. Arrowheads denote specific protein-DNA complexes.