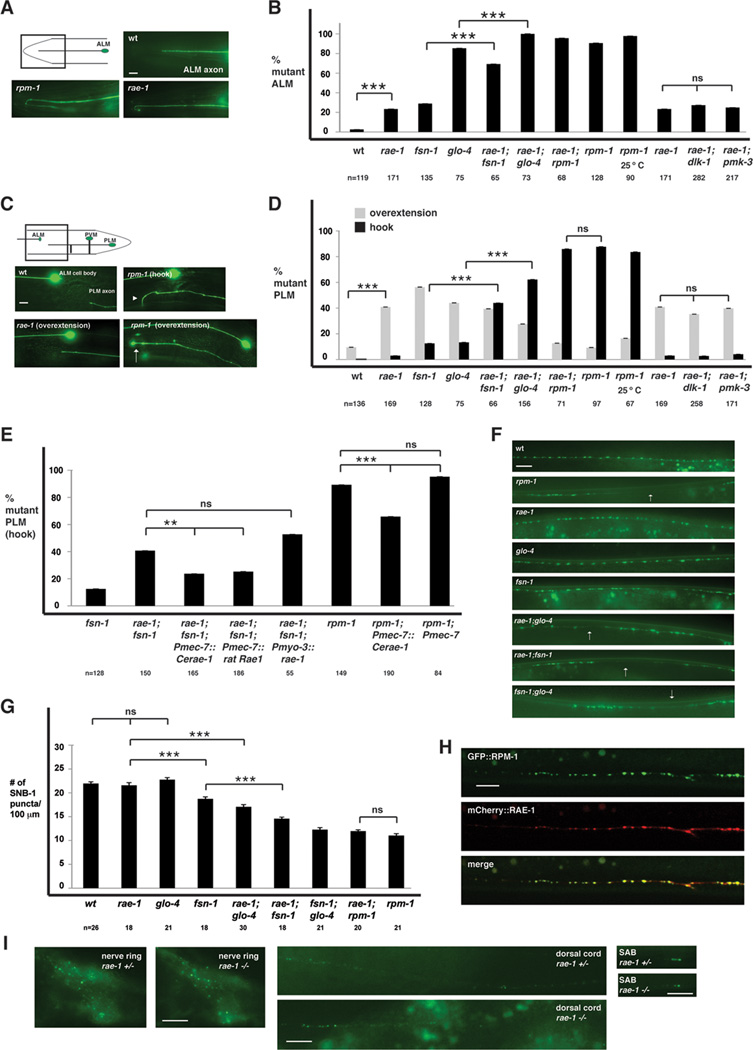
Figure 3.
rae-1−/− mutants have defects in axon termination and synapse formation. A and C, mechanosensory neurons (ALM and PLM) were visualized using muIs32. A, ALM axon termination defects in rpm-1−/− and rae-1−/− animals. B, quantitation of ALM axon termination defects for the indicated genotypes. C, PLM axon termination defects in rpm-1−/− and rae-1−/− animals. The arrowhead highlights an example of the hook and overextension (hook) defect in rpm-1 mutants and the arrow highlights the less penetrant overextension defect in rpm-1−/− mutants. D, quantitation of PLM axon termination defects for the indicated genotypes. E, expression of C. elegans rae-1 or a cDNA encoding rat Rae1 in the mechanosensory neurons rescues the axon termination defects (hook) in the PLM neurons of rae-1−/−;fsn-1−/− animals. Overexpression of rae-1 was also sufficient to partially rescue defects in rpm-1−/− animals. For all extrachromosomal arrays, data from 4–10 independently derived transgenic lines was pooled. F, the presynaptic terminals of the DD neurons (dorsal cord) were visualized using SNB-1::GFP. Arrows highlight examples of gaps where presynaptic terminals are absent. G, quantitation of synapse formation defects in the DD neurons. H, confocal microscopy was used to visualize the dorsal cord of transgenic animals that express RPM-1::GFP (juIs77) and mCherry::RAE-1 (bggEx76) in the GABAergic motor neurons using the unc-25 promoter. mCherry::RAE-1 forms discrete puncta in the dorsal cord that colocalize with RPM-1::GFP puncta in the perisynatic zone of presynaptic terminals. I, Epifluorescent microscopy was used to visualize RPM-1::GFP driven by its own promoter (juIs58) in the nerve ring, dorsal cord, and SAB neurons of rae-1+/− or rae-1−/− animals. No difference in the levels and localization of RPM-1::GFP were observed in rae-1 mutants compared to heterozygous animals. Analysis of axon termination was done at 23°C, and analysis of synapse formation was done at 25°C. Scale bars are 10µm. For B and D, "n" is the number of individual mechanosensory neurons that were scored. For G, "n" is the number of images of the dorsal cord that were quantified. For axon termination defects, error bars represent the standard error, and significance was determined using a two-tailed Fisher's exact test. For synapse formation defects, error bars represent standard error of the mean, and significance was determined using a t test. ** p<0.005, *** p<0.001, and ns=not significant.