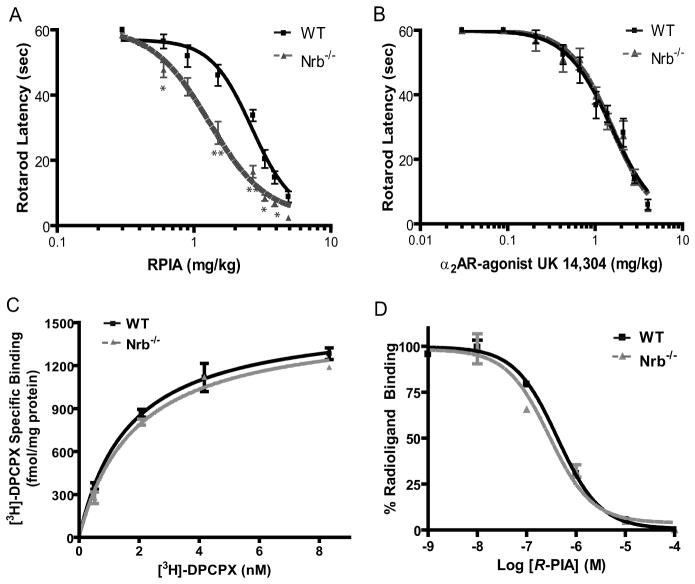
Figure 4.
Neurabin attenuates A1R-mediated responses in vivo. A, Neurabin-deficient mice are more sensitive to R-PIA-elicited sedation, as assessed by rotarod latency. The EC50 values for sedation in Nrb−/− (n=8) and corresponding WT littermates (n=5) are 1.29 and 2.64 mg/kg, respectively. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. B, The α2AR-agonist, UK14,304, induces comparable sedation responses in both WT and Nrb−/− mice as assessed by rotarod latency. n=5 for both WT and Nrb−/− mice. Error bars represent mean±SEM. C, The density of A1Rs is indistinguishable in brain membrane preparations obtained from WT and Nrb−/− mice as measured by saturation binding assays. Values represent mean ± SEM; n=3 for each genotype. The Bmax values predicted by nonlinear regression fit for the A1R in WT and Nrb−/− brain homogenates are 1547 ± 90 and 1515 ± 76 fmole/mg protein, respectively. D, The intrinsic affinity of the A1R for R-PIA in brains of WT mice is similar to that in brains of Nrb−/− mice. Competition binding assays were performed in the presence of 100 μM Gpp(NHp). Binding of the [3H]DPCPX radioligand is given as a percentage of binding without competitors. Values represent mean ± SEM; n=3 for each genotype. The IC50 values predicted for R-PIA in competition for radioligand binding in WT and Nrb−/− brain homogenates are 0.41±0.11 and 0.29±0.12 μM, respectively.