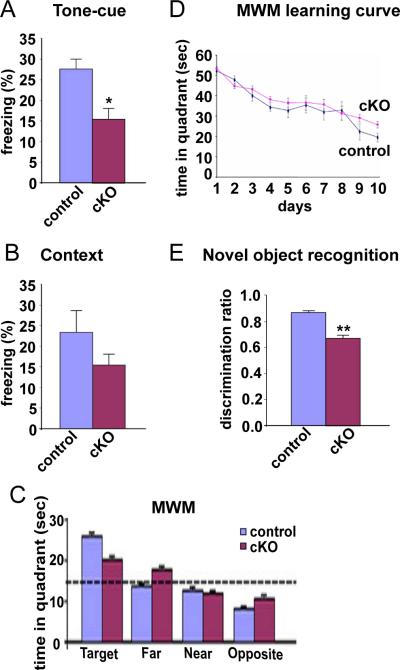
Figure 8.
Impact of TrkA loss in BFCNs on cognitive activity. A, Tone-cued fear conditioning. The percentage of freezing of control=27.19 ± 4.41%; TrkAcKO = 15.24 ± 4.01% (n=12 per genotype, p=0.015). B, Contextual fear conditioning. The percentage of freezing of control =23.13 ± 6.77%; TrkAcKO =15.28 ± 3.20% (n=12 per genotype, p=0.247). C, Morris water maze (MWM). The time in the target quadrant of control = 25.72 ± 1.87 sec; TrkAcKO = 19.96 ± 2.23 sec (n=16 for control; n=17 for TrkAcKO, p=0.058). D, Learning curve from MWM test showed no statistical difference between control and TrkAcKO mice. E, Novel object recognition. The discrimination ratio of control = 0.867 ± 0.025; TrkAcKO = 0.673 ± 0.054 (n=17 per genotype, **p=0.002). For the fear conditioning and MWM tests, male mice were tested at 6 months of age. For the novel object recognition task, male mice were tested at 2 months of age.