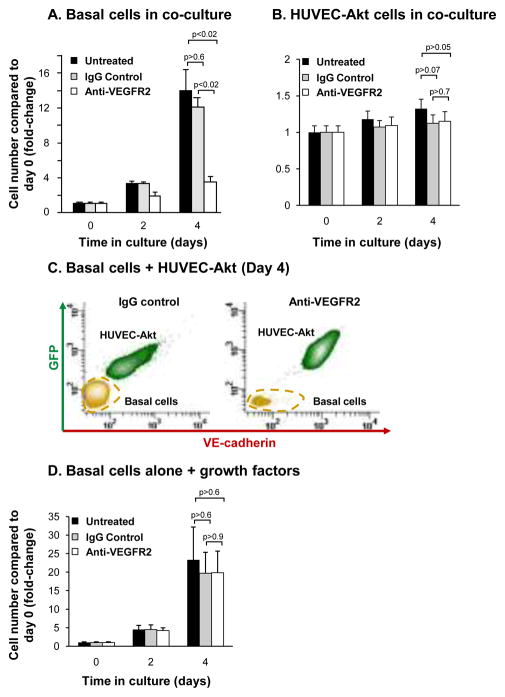
Figure 8.
Inhibition of VEGFR2 signaling suppresses endothelial cell dependent proliferation of airway basal cells. A–B. Human airway basal cells were co-cultured with human umbilical vein endothelial cells activated with Akt (HUVEC-Akt) in cytokine- and serum-free conditions and incubated with control IgG or blocking monoclonal antibodies against VEGFR2. Data shown is the average of 3 independent experiments. A. Basal cells; B. HUVEC-Akt cells. C. Representative flow cytometric analysis of human airway basal cell and HUVEC-Akt cell populations at day 4 of co-culture following incubation with control IgG or anti-VEGFR2. HUVEC-Akt cells were determined as the GFP+VE-cadherin+ population, and the GFP−VE-cadherin− population quantified as basal cells. D. Human airway basal cells were cultured in growth media and incubated with control IgG or blocking monoclonal antibodies against VEGFR2. Data shown is the average of 3 independent experiments. For all panels, shown is untreated (black), IgG control (gray), and anti-VEGFR2 (white).