Figure 4. Cx36 forms gap junctions between red/green cones.
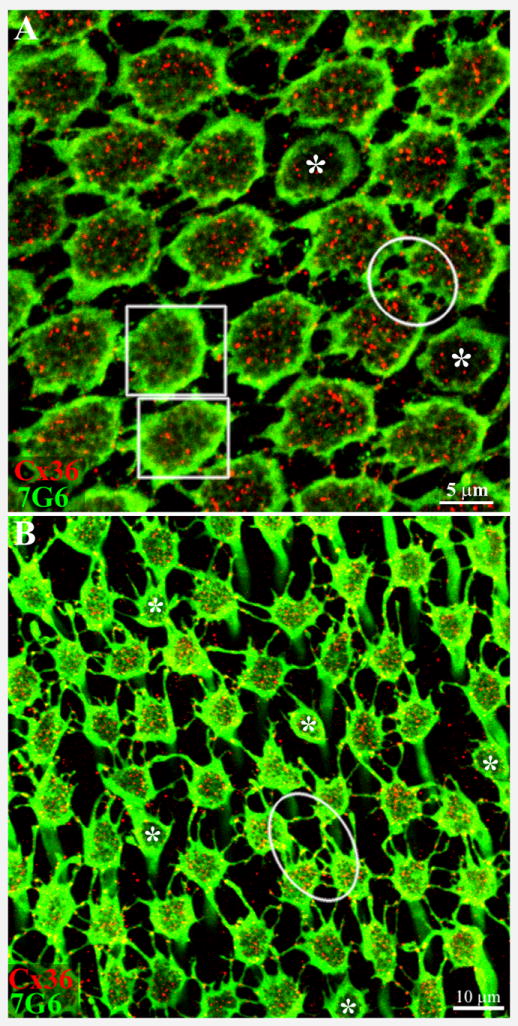
Macaque retina was viewed in wholemount with the level of focus at the base of the cone pedicles in the OPL. A. In central retina, cone pedicles stained for 7G6 (green) were tightly packed, frequently with direct contacts between neighboring pedicles. In addition, there are many small processes or telodendria, which contact adjacent pedicles. The Cx36 labeling within the perimeter of each cone pedicle is due to the presence of Cx36 gap junctions beneath the cone pedicle (red). In two pedicles (+) (boxes) that are slightly higher, the synaptic invaginations (holes) in the pedicle base begin to blur and fill in and the Cx36 labeling underneath is markedly reduced. Two smaller, potentially blue cone pedicles are marked with asterisks. It should be noted that Cx36 plaques occur at nearly all direct or telodendrial contacts between red/green cone pedicles. For example, a well-labeled group of Cx36 gap junctions are stained within the circle. 6 × 0.4 μm optical sections.
B. In peripheral retina, the cone pedicles are more widely spaced and the telodendria are more obvious. Again, Cx36 plaques occur at telodendrial contact points between neighboring cone pedicles (oval). A few presumed blue cone pedicles, marked with asterisks, have very few telodendria or Cx36 contacts. 6 × 0.4 μm optical sections.
