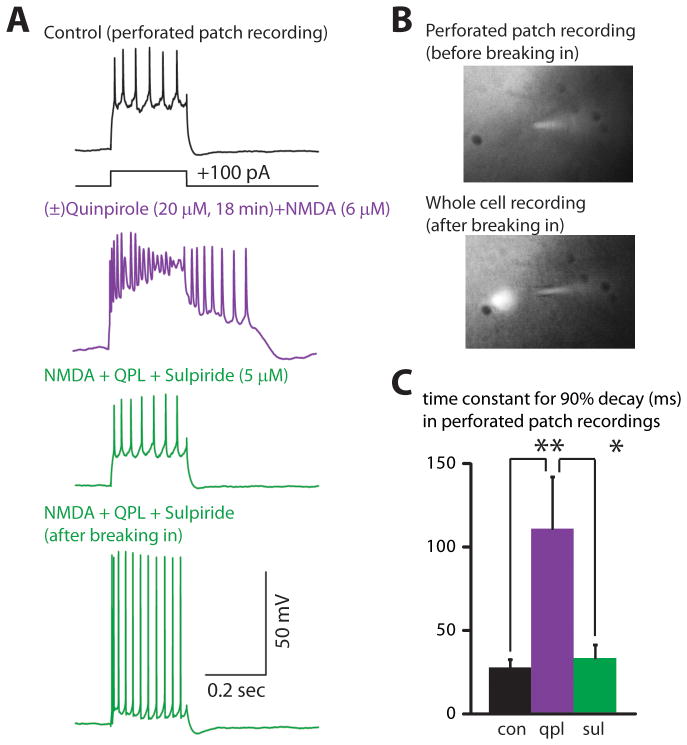
FIGURE 6. Quinpirole also induces an afterdepolarization during perforated-patch recordings from type A neurons.
(A) Recordings from a type A neuron in perforated-patch configuration (top three panels) showing the quinpirole-induced afterdepolarization that occurs in the presence of NMDA, and is reversed by sulpiride. The bottom panel shows a recording from the same neuron after breaking in and shifting to a whole cell recording. (B) Fluorescent dye in the recording pipette was excluded from the neuron while in the perforated-patch configuration (top image), but entered the neuron after breaking in and shifting to a whole cell configuration (bottom image). (C) Summary data showing that (±)quinpirole (20 μM) plus NMDA (6 μM) prolongs the time constant for the membrane potential to return to baseline following depolarizing current pulses (350 pA, 250 msec), and that this is reversed by the addition of sulpiride (5 μM) (n=5). * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01.