Figure 5.
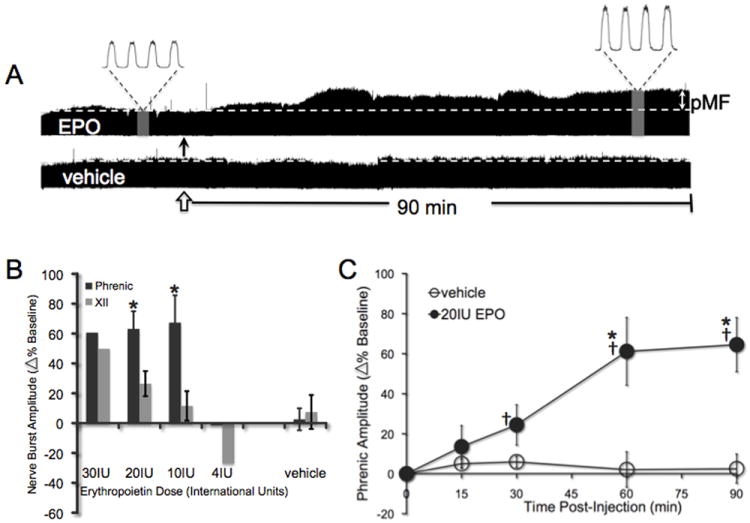
Intrathecal EPO elicits a long-lasting phrenic motor facilitation. A) Representative compressed phrenic neurograms showing either phrenic motor facilitation (pMF) after EPO injection (closed arrow) or no facilitation after vehicle injection (open arrow). B) Preliminary dose response curve for EPO; the dose subsequently used confers pMF without effects on hypoglossal (XII) activity. (*significantly different from XII motor facilitation at same dose; all p<0.001). C) The amplitude of integrated phrenic bursts increases from baseline after 10μl (20IU) EPO injections (n=8; solid circles), and is significantly different from vehicle controls at the same time point (10μl; n=6; open circles). All values are change in phrenic burst amplitude as percent baseline. Mean values ± 1 S.E.M. †: significantly different from baseline (all p<0.05); *significantly different from vehicle at the same time (all p<0.05).
