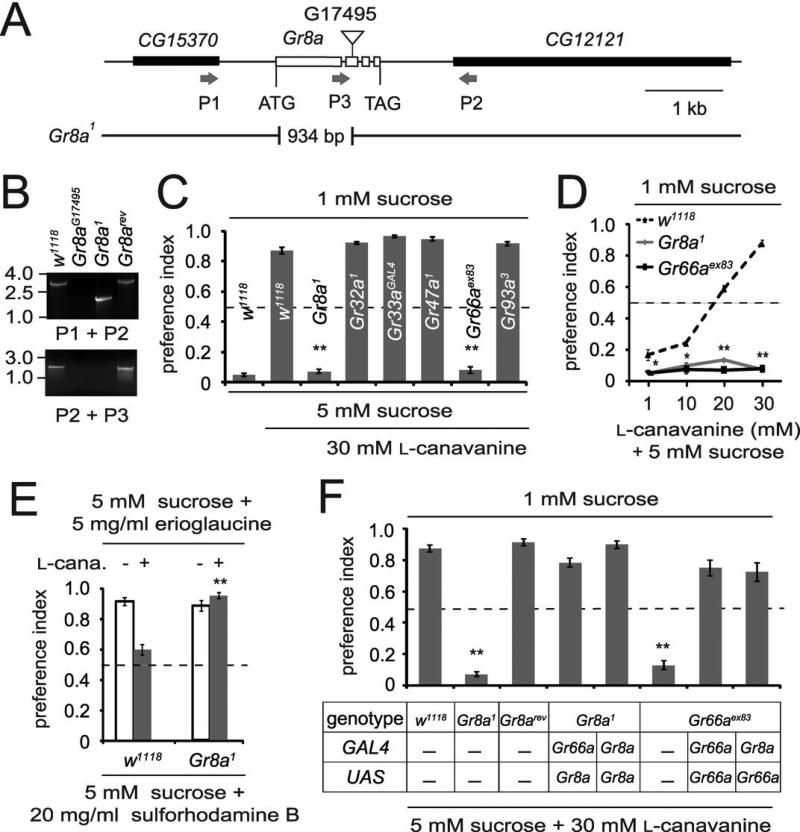
Figure 2.
GRs required for l-canavanine avoidance. A, Physical map of the Gr8a genomic region. The P-element (G17495) that inserted in the Gr8a coding region is indicated by the inverted triangle. The deletion and precise excision were confirmed using the indicated PCR primers (arrows) to amplify genomic DNA (P1, P2 and P3), followed by DNA sequencing. B, PCR analyses of genomic DNA. The PCR products were generated using the indicated fly stocks and PCR primer pairs, and fractionated on an agarose gel. C, Screen for Grs required for l-canavanine avoidance. The two-way choice tests were performed using the indicated chemicals and fly stocks. n=5-15. D, Dose-avoidance relationship determined using the two-way choice behavioral assay. Flies of the indicated genotypes were tested using l-canavanine over a range of concentrations (1-30 mM). n=4-11. E, Two-way choice assays using 5 mM sucrose plus 5 mg/ml erioglaucine (in the presence or absence of 30 mM l-canavanine) versus 5 mM sucrose plus 20 mg/ml sulforhodamine B. F, Rescue of l-canavanine avoidance defects by expressing wild-type Gr transgenes in GRNs using the GAL4/UAS system. n=6-13. The error bars indicate SEMs. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.