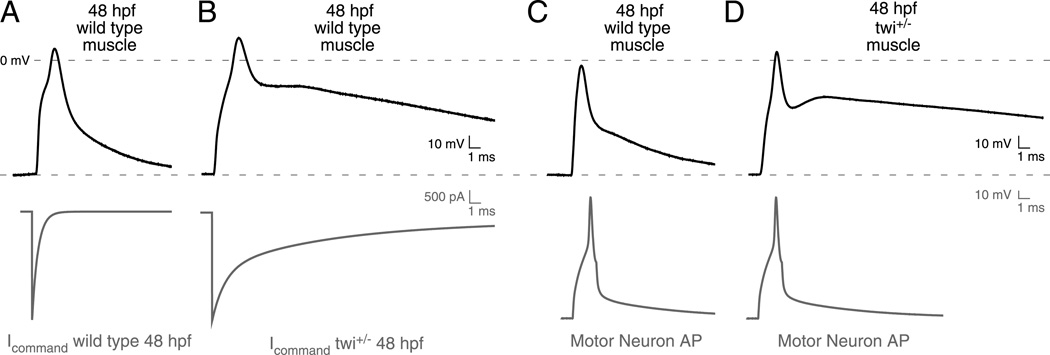
Figure 2. Effect of prolonged synaptic currents on post-synaptic potential.
A,B, Representative action potential waveforms recorded from 48 hpf wild type fast muscle were elicited using voltage command waveforms based on the average synaptic current decays for wild type (A) and twi+/− (B) shown in Figure 1. The command waveforms are shown in red and the associated muscle responses are shown in black (n=5 cells; Between 12 and 20 action potentials were averaged for each cell). C,D, Paired current clamp recordings of motorneuron (red) and muscle action potentials (black) for 48hpf wild type (C; n= 4 pairs; 7–28 action potentials per cell) and twi+/− (D; n=6 pairs; 8–26 action potentials per cell) muscle.