Figure 1.
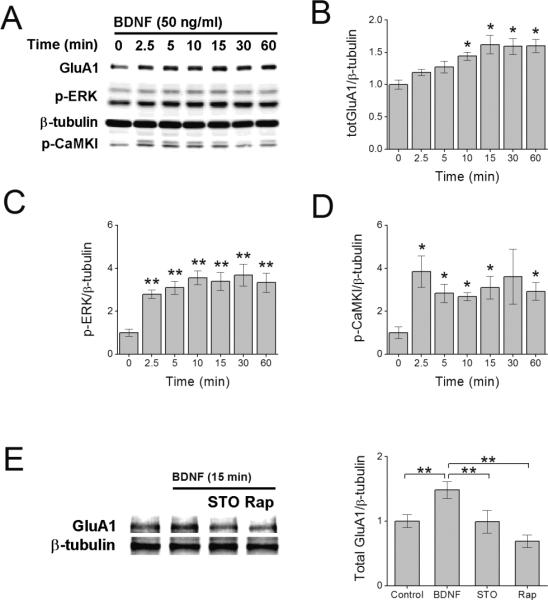
BDNF-induced increase in total GluA1 protein requires CaMKK. Representative immunoblot of hippocampal cell lysates illustrating the increase in total GluA1 (A, B), phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK) (C), and CaMKK-mediated phosphorylation of CaMKI (p-CaMKI) (D) following increasing times of BDNF treatment. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 5 from 5 independent experiments). *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc test. E, Representative immunoblot (left panel) and quantification (4 independent experiments) of total GluA1 protein following 15 min of BDNF treatment in the absence or presence of 10 μM STO-609 (STO, CaMKK inhibitor) or 1 μM rapamycin (Rap, mTORC1 inhibitor). Error bars indicate SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by Student's t test. In panels A and E, β-tubulin is shown as loading control.
