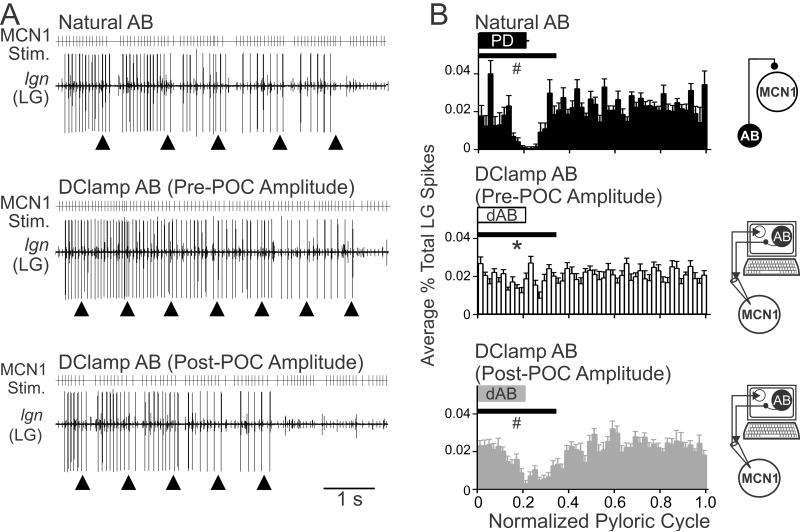
Figure 8.
POC-modulation of the AB feedback synapse to MCN1 is necessary for the POC-triggered gastric mill motor pattern. A, MCN1 was stimulated (MCN1 Stim.) using the activity patterns recorded in response to natural AB feedback (top), pre-POC amplitude dAB (middle), and post-POC amplitude dAB (bottom) (see Methods). The pre-POC amplitude dynamic clamp stimulation pattern did not elicit pyloric-timed interruptions in the LG bursts, whereas the other two conditions did elicit pyloric-timed pauses in LG firing such as are characteristic of the POC-gastric mill rhythm. Arrowheads indicate onset of natural or dynamic clamp AB activity. B, The average percent of LG action potentials per bin and the phase of AB/PD activity are plotted against the normalized pyloric cycle for three conditions: (top) natural AB, (middle) pre-POC amplitude dAB, and (bottom) post-POC amplitude dAB. MCN1 stimulation patterns based on the MCN1 activity pattern during natural AB inhibition and post-POC amplitude dAB inhibition resulted in a smaller percentage of LG spikes during the initial 35% of the normalized pyloric cycle, relative to the MCN1 pattern occurring during the pre-POC amplitude dAB inhibition. The horizontal bars indicate the region of statistical analysis. Schematics to the right of each panel indicate whether natural AB inhibition was present or dAB inhibition was injected into MCN1. Arrows as in Fig. 7. *p<0.05 compared to natural AB, #p<0.05 compared to pre-POC dAB.