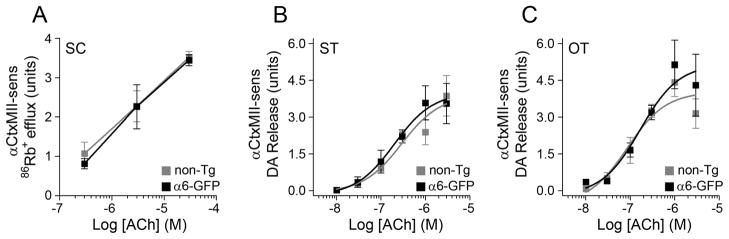
Figure 3.
Normal α6* nAChR function in α6-GFP transgenic mice. A. Normal Rb+ efflux in α6-GFP transgenic mice. A crude synaptosomal pellet was prepared from α6-GFP and their non-transgenic littermates, followed by Rb+ loading and stimulation of Rb+ efflux by ACh application. Rb+ efflux sensitive to αCtxMII (which includes α6-dependent efflux) is shown for 0.3 μM, 3 μM, and 30 μM ACh. B, C. Normal DA release in α6-GFP transgenic mice. Dorsal striatum (‘ST’; B) and olfactory tubercle (‘OT’; C) were dissected from α6-GFP and their non-transgenic littermates, followed by preparation of synaptosomes. Synaptosomes were loaded with [3H]-DA and stimulated with a range of ACh concentrations (10 nM, 30 nM, 100 nM, 300 nM, 1 μM, and 3 μM) in the presence and absence of αCtxMII. Data were fitted to the Hill equation, and αCtxMII-sensitive concentration response curves are shown for ST (B) and OT (C).