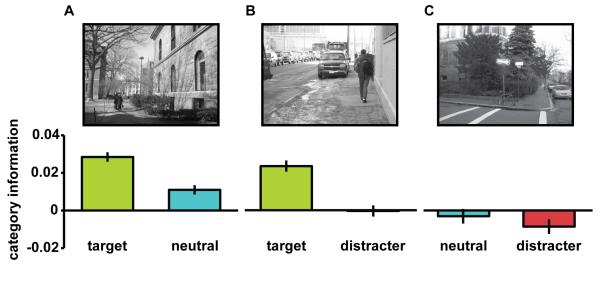
Figure 5. Category information in scenes depicting two categories.
Examples for two-category scenes are shown for a run in which people served as the target category while trees constituted the neutral category and cars the distracter category. Category information was calculated separately for the two categories embedded in the scene. The correlation between the scene and the category not present in the scene was subtracted from the correlation between the scene and one of the two categories present in the scene. (a) In T-N scenes both the target and the neutral category were processed to the category level. (b) In T-D scenes the target but not the distracter category was processed to the category level. (c) Information values did not differ for the neutral and distracter category in N-D scenes. Error bars denote ± s.e.m. corrected for within-subject comparisons.