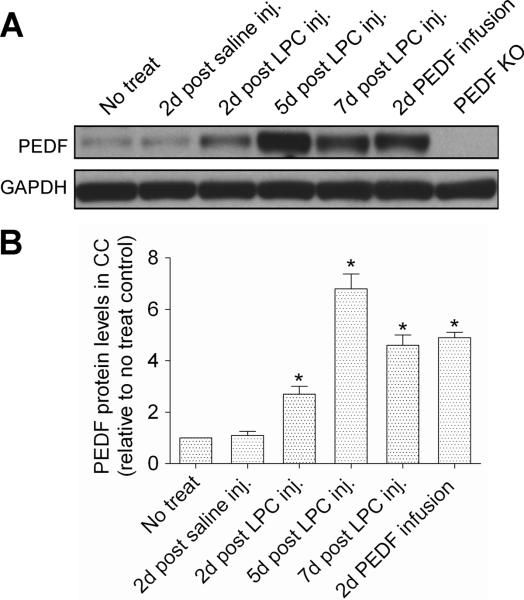
Figure 10. Regulation of PEDF protein expression in lysolecithin-induced demyelinative corpus callosum.
Mice received no treatment, saline or lysolecithin (LPC) injections to corpus callosum (CC), or PEDF infusion (300ng per day) to corpus callousm. Protein extracts from ipsilateral corpus callosum were analyzed for PEDF expression by Western blots. (A) Representative Western blot showing robust upregulation of PEDF expression in the corpus callosum after lysolecithin injection. Specificity of the PEDF antibody used for Western blotting was confirmed by the absence of immunoreactive PEDF in homozygous PEDF knockout mice. (B) Densitometiric quantification demonstrated that PEDF contents were 2.7, 6.7 and 4.6 fold higher in lysolecithin-lesioned than intact corpus callosum on days 2, 5, and 7 post-lysolecithin injection, respectively. In non-lesioned mice, 2 days of intracerebral recombinant PEDF infusion raised corpus callosum PEDF content by 4.9 fold. Results are means +/− SEM (n = 3 mice/point). * significantly elevated (p<0.001, Student's t test) over level in intact corpus callosum.