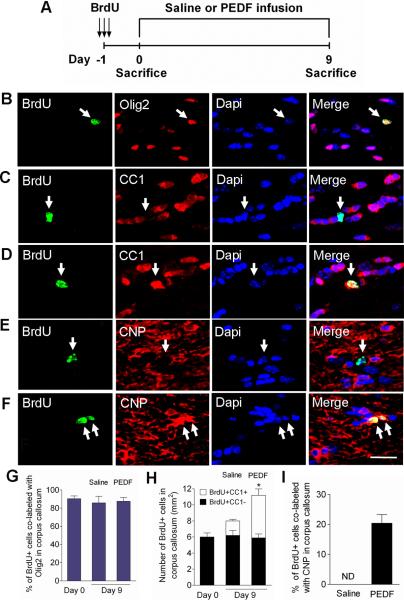
Figure 7. PEDF enhances oligodendrocyte production and maturation of cycling OPCs in the adult corpus callosum.
(A) Experimental design: adult wild type mice received three consecutive administrations of BrdU (100mg/kg body weight ip) at 6 hour intervals to label cycling OPCs in the corpus callosum, followed by saline- or PEDF- (300ng per day) intracerebral infusion for 9 days. (B–C) Confocal images of cells double-immunostained for BrdU and Olig2 (B) or CC1 (C) at day 0. (D–F) Confocal images of cells double-immunostained for BrdU and CC1 (D) or CNP (F) in PEDF-infused, and for BrdU and CNP (E) in saline-infused corpus callosum at day 9. (G) Percentages of BrdU+ cells that were co-labeled with Olig2 at day 0 and day 9. The vast majority of cycling cells in the corpus callosum were Olig2+. (H) Quantification for cells co-immunolabeled for BrdU and CC1, a marker for mature oligodendrocytes, in the corpus callosum at day 0 and day 9. At day 0, BrdU labeled OPCs did not express CC1. By day 9, CC1+ mature oligodendrocyte had been produced from BrdU+ OPCs after both saline- and PEDF- infusion, but significantly more with PEDF infusion. (I) Percentages of BrdU+ cells co-labeled with CNP in saline- and PEDF-infused corpus callosum demonstrating that PEDF robustly promoted terminal maturation of newly born OPCs. ND = non-detected. (B–F) Arrows indicate BrdU+ cells co-immunostained with oligodendroglial markers. Scale bar = 35μm. Results are means +/− SEM (n= 3 brains, * P<0.01: an increase in the number of BrdU+CC1+ cells in between saline- vs. PEDF-infused corpus callosum at day 9, Student's t test).