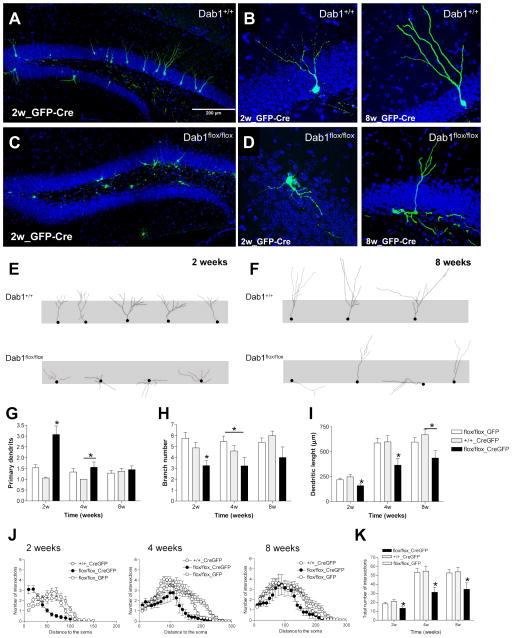
Figure 4. Dab1 deficiency leads to severe morphological alterations of adult-generated neurons.
A–D) Representative images of adult-generated neurons infected with GFP- and Cre-expressing retrovirus in Dab1+/+ (wt) and Dab1fl/fl (fDab1) mice 2 weeks post-surgery. E–F) Tracings of adult-generated neurons at 2- and 8-week post-surgery in Dab1+/+ and Dab1fl/fl mice. G–I) Quantification of morphological parameters of adult-generated neurons infected with GFP only (GFP) or Cre and GFP (CreGFP) retroviruses in Dab1+/+ and Dab1fl/fl mice. The number of primary dendrites in fDab1-GFP-Cre neurons was higher than in control groups at 2 weeks post-surgery (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05) and in the wt-CreGFP group at 4 weeks (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05). The number of branches in fDab1-GFP-Cre neurons was greater than in control groups at 2 weeks post-surgery (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05) and in the fDab1-GFP group at 4 weeks (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05). The dendritic length of fDab1-GFP-Cre neurons was higher than in control groups at 2 and 4 weeks post-surgery (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05) and in the wt-CreGFP group at 8 weeks (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05). J–K) Sholl analysis. Dab1-deficient neurons have lower numbers of intersections than WT neurons at all the time points studied (ANOVA: p<0.05; posthoc: p<0.05).