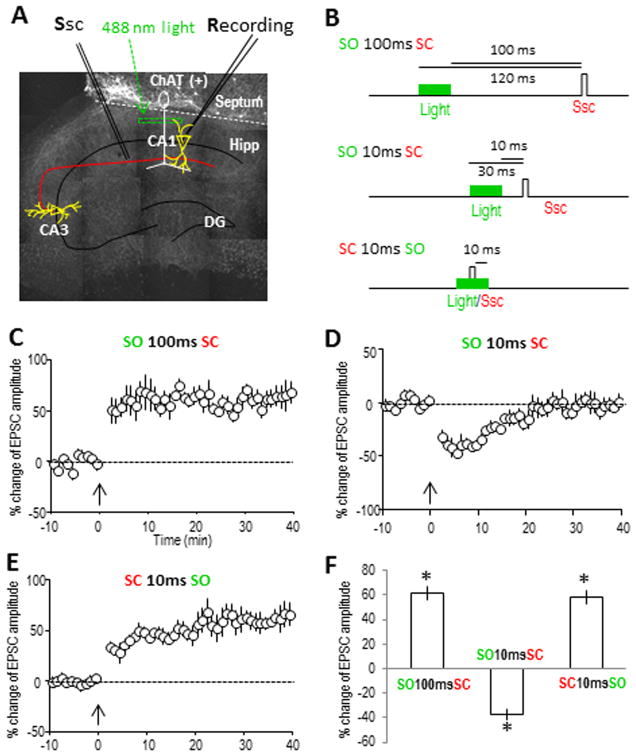
Fig. 2. Optogenetically-activated cholinergic inputs induce similar timing-dependent hippocampal plasticity in septo-hippocampal co-cultures as in acute hippocampal slices.
(A) Cholinergic projections (infected with ChR2) in a small region in the hippocampal SO were exposed to 488 nm light (20 ms) for timed activation. (B) Three different intervals for pairing cholinergic (SO) and SC pathways were used to induce plasticity, as used in acute hippocampal slices previously. (C) LTP was induced by optically activating the cholinergic input 100 ms before stimulating the SC. The pairing protocol was introduced at the time point of 0 min as indicated by the arrow. (D) STD was induced by activating the cholinergic input 10 ms before the SC. (E) LTP was induced by pairing the SC 10 ms before optically activating the cholinergic input. (F) Bar graph showing the amplitude changes of the three types of synaptic plasticity, analyzed at 30 min for LTP and 10 min for STD. *p<0.001, as compared with before pairing, Student t-test, n=5 in each group.