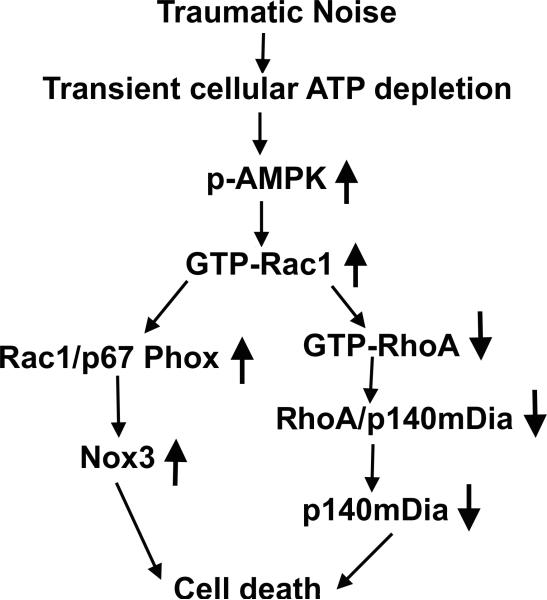
Figure 12.
Summary of the molecular pathway. Traumatic noise causes transient cellular energy depletion in the inner ear, as shown by an increase in expression of p-AMPKα in sensory hair cells, and consequently activates Rho GTPase pathways, as determined by GTP-Rac1 and GTP-RhoA analysis. The increase in activated Rac1 leads to ROS formation, as shown by an increase in Nox3 expression through activation of NADPH oxidase (as determined by assessment of Rac1/p67 phox complexes), thus promoting hair cell death. Additionally, increased active Rac1 also leads to a decrease in activated RhoA levels, which decreases the formation of complexes of RhoA/p140mDia and the levels of diaphanous protein and leads to hair cell death.