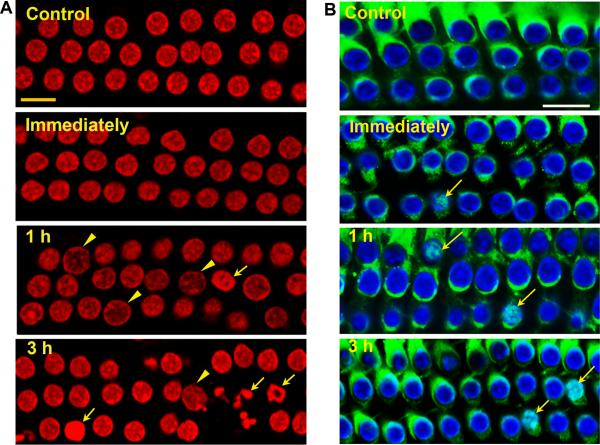
Figure 2.
(A) Apoptotic and necrotic outer hair cell death in the basal segment of the cochlear epithelium: Control cochleae and those harvested immediately after noise exposure showed no outer hair cells displaying features of apoptotic or necrotic death. At 1 and 3 h post-noise exposure cells with swollen necrotic (arrowheads) or fragmented apoptotic nuclei (arrows) were present, but more cells with apoptotic nuclei were observed at 3 h than 1 h post-noise exposure. Red: propidium iodide (PI) staining for nuclei. (B) Translocation of Endo G to the nuclei of some outer hair cells in the basal segment of the cochlear epithelium. Immunofluorescence of Endo G on surface preparations from control mice showed Endo G in outer hair cells, but not in their nuclei. Immediately, 1 h, and 3 h post-exposure, Endo G translocated into some nuclei of outer hair cells (arrows). Green: Endo G, blue: Hoechst 33342 staining for nuclei.
All images were taken from the upper basal turn and each figure is representative of 3 individual mice for each condition. “Immediately” indicates samples obtained immediately after 2 h BBN noise exposure at 106dB; 1 h and 3 h indicate samples obtained 1 and 3 h post-noise exposure. Scale bars = 10 μm.