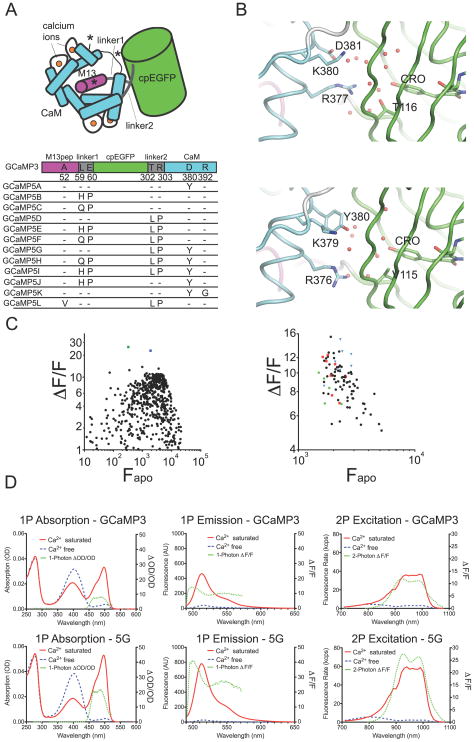
Figure 1. Design of GCaMP5s.
(a) Schematic of the GCaMP3 structure with sites of engineering shown. (b) Structural effects of the D381Y mutation (D380Y in GCaMP3 numbering). Chromophore environment at the cpGFP/CaM interface in GCaMP2 (top panel, PDB 3EVR)(Akerboom et al., 2009) and GCaMP5G (bottom panel, PDB 3SG4) structure reported here. Structures are shown as cartoon and sticks colored by domain (cpGFP: green, linker: white, CaM: cyan). Selected portions of the model around the GFP chromophore (CRO) are represented as sticks with ordered water molecules represented as red spheres. (c) (ΔF/F)max versus Fapo for both linker 1 variants of GCaMP3 (left panel) and linker 2 variants of GCaMP3 (right panel) in bacterial lysate. In the left panel, the green square denotes L1-Gln-Pro, the blue square denotes L1-His-Pro. In the right panel, linker variants L2-Pro-X are depicted as red squares, L2-X-Pro as blue triangles, and original GCaMP3 linker variants (L2-Thr-Arg) as green dots. (d) 1-Photon absorption (left panels), 1-Photon emission (middle panels) and 2-photon excitation (right panels) spectra of both GCaMP3 (top three panels) and GCaMP5G (bottom three panels). Calcium-free spectra are depicted by dashed blue lines, and calcium-saturated spectra by solid red lines. Dashed green lines depict (ΔF/F)max, plotted on the right axis.