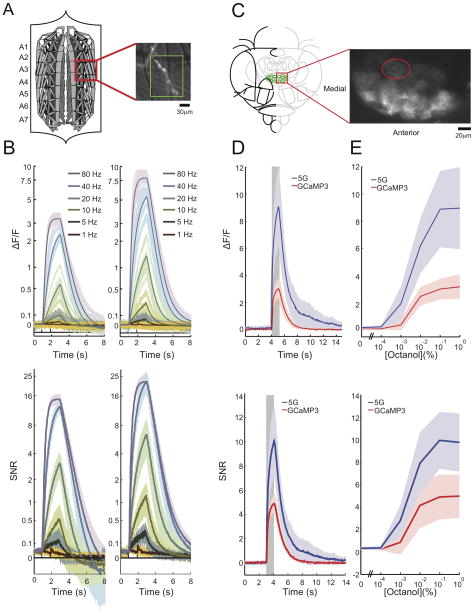
Figure 6. GCaMPs in Drosophila.
(a) Schematic of larval NMJ preparation, and close-up of Type 1b boutons from muscle 13 (segments A3–A5) used for wide-field imaging (scale bar: 30 μm). (b) Single trials of electrically-evoked Ca2+ transients from wide-field imaging in the Drosophila larval NMJ. Fluorescence changes (ΔF/F) from presynaptic terminals obtained by delivering 2 seconds of electrical stimulus at different frequencies. Left panel: GCaMP3, right panel: GCaMP5G. (c) Two-photon imaging frame scan of projection neurons (PNs) innervating the DC1 glomerulus in the adult fly antennal lobe (dorsal view, scale bar: 20 μm). (d). The mean of 5 replicate stimulations from 6 antennal lobes (5 animals) is shown along with the s.d. (between antennal lobe means). Response to a 0.1% octanol, 1-second odor pulse from DC1 PNs. (e). Mean octanol response from PNs from DC1 glomerulus (averaged over 5 flies) to increasing concentration. All panels show mean ± s.d.