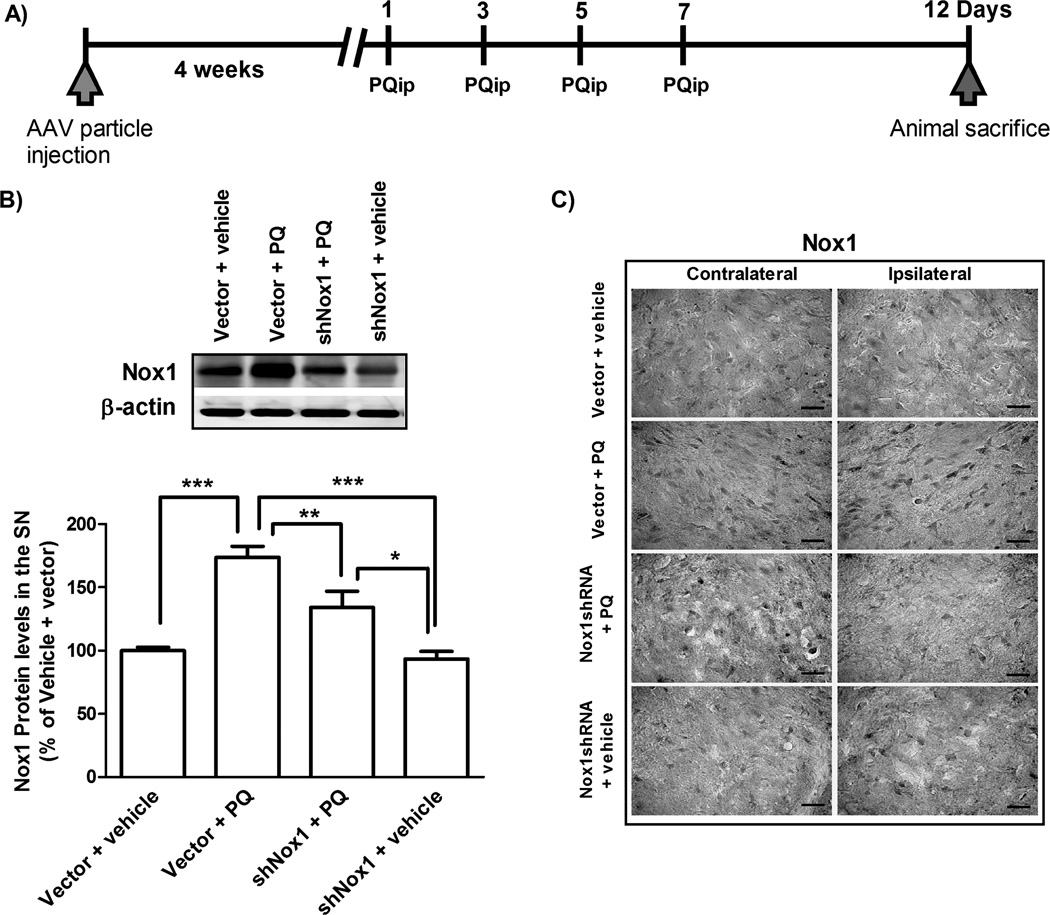
FIG. 7. Selective Nox1 targeting by AAV-mediated Nox1 knockdown in the rat SN.
(A) AAV2 viral particles and PQ injection paradigm diagram. To knockdown Nox1 in the SN, AAV2 particles harboring Nox1 shRNA were stereotaxically injected into the SN. PQ i.p. injections were carried out 4 weeks after AAV2 delivery. Rats were divided into four groups. Group vector + vehicle: stereotaxic injection of AAV2 particles containing GFP vector and then vehicle (saline) i.p. injection; group vector + PQ: stereotaxic injection of AAV2 particles containing GFP vector and then PQ i.p. injection; group shNox1 + PQ: stereotaxic injection of AAV2 particles harboring Nox1 shRNA-GFP and then PQ i.p. injection and group shNox1 + vehicle: stereotaxic injection of AAV2 particles harboring Nox1 shRNA-GFP and then vehicle i.p. injection. Animals were given a total of four i.p. injections of either vehicle or PQ (10 mg/kg of b.w.) every two days. All groups were sacrificed 5 days post last injection. (B) Representative immunoblot and quantitative analysis of Nox1 protein determined in total lysates of rats ipsilateral SN tissues. β-actin was used as an internal control. Nox1 protein levels were quantified using Quantity One software and normalized against β-actin. The results are expressed as percentage of vector + vehicle. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s Multiple Comparison Test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (C) Representative photomicrographs of Nox1-immunoreactivity in the SN sections of the contralateral and ipsilateral sides of brain sections. Scale bars = 50 µm.