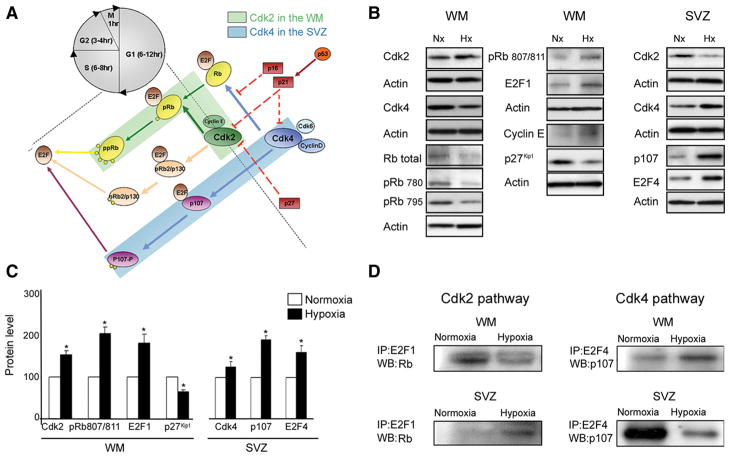
Figure 8.
Distinct pathways responsible for cell proliferation in white matter and SVZ after hypoxia. Cdk2 and Cdk4 are activated by hypoxia in white matter and SVZ, respectively. A, Schematic drawing of the network of cell cycle proteins involved in proliferation in white matter and SVZ. B, Western blot analysis of white matter and SVZ tissue dissected from P18 normoxic and hypoxic mice. Expression of Cdk2 and Cdk4, cyclin E, total Rb, pRb(Ser780), pRb(Ser795), pRb(Ser807/811), p107, E2F1, E2F4, and inhibitor, p27 Kip1, was analyzed. C, Graphs represent an elevated expression of Cdk2, pRb807/811, E2F1, and reduced p27 Kip1 in white matter after hypoxia. Higher levels of Cdk4, p107, and E2F4 were found in SVZ after hypoxia, compared with normoxia. Western blot analysis was performed on four independent WM and SVZ samples for each condition (*p < 0.05, t test). Actin was used as a loading control. D, Immunoprecipitation assays performed on white matter and SVZ from normoxic and hypoxic P18 tissue. Rb–E2F1 and p107–E2F4 complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-E2F1, and anti-E2F4 antibodies, respectively, and probed on Western blot with anti-Rb and anti-p107 antibodies. At P18, Rb expression was lower in hypoxic compared with normoxic white matter, while lower p107 expression was observed in hypoxic SVZ. Analysis was repeated on four independent WM and SVZ specimens for each condition. Western blot results are shown from a representative experiment. Error bars indicate SEM.