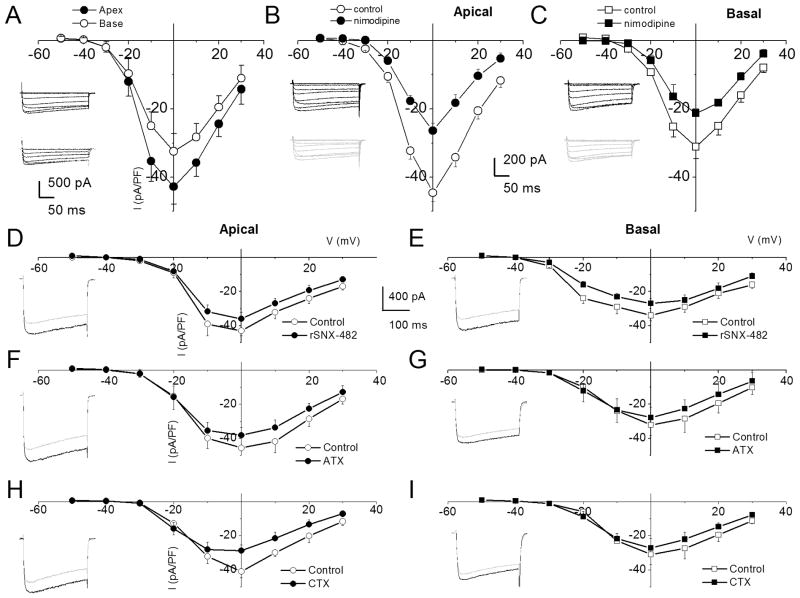
Figure 3. Characteristics of Ca2+ currents in 3-month old spiral ganglion neurons from apical and basal turns of the cochlea, and the effects of Ca2+ current blockers.
A Family of inward Ca2+ currents from apical SGN elicited from a holding potential of −70 mV to step potentials from −50 to 30 mV in 10-mV increments, (inset at the left panel). A similar voltage pulse protocol was applied to generate Ca2+ current traces from basal SGNs (inset at the right panel). Peak Ca2+ current density-voltage relations for apical (●) and basal (○) SGNs. At voltages (−10 to 10 mV), there were significant differences between apical and basal Ca2+ current-densities (* = p < 0.05; n = 17). B The dihydropyridine antagonist, nimodipine, blocks a component of whole cell Ca2+ currents in SGNs. Current traces recorded from neurons isolated from apical (inset, upper (control) and lower (nimodipine) panels) segments of the cochlea. Perfusion of external solution containing 10 μM nimodipine resulted in a reduction of the Ca2+ currents. The corresponding current density-voltage relations for apical (B) and basal (C) SGNs (n = 9). The control data is illustrated with black lines and symbols and the residual current after nimodipine block is shown in blue lines and symbols. D The current-density-voltage relations were generated before (in black lines and symbols) and after (in blue lines and symbols) application of Ca2+ current blockers, rSNX-482, for R-type (D–E), ω-Agatoxin IVA (ATX), for P/Q-type (F–G), and ω-Conotoxin MVIIA (CTX) for N-type (H–I) currents. D–E Shown are the current-density-voltage relations for control (in black) and the remaining current-density after application of toxins (in blue) for apical (D) and basal (E) SGNs (n = 6). The insets on the left panels of the plots are representative current traces recorded from a holding voltage of −70 mV to a step voltage of 0 mV. F–G Similar data obtained upon recording control Ca2+ currents and after application of the P/Q-type Ca2+ current blocker, 1 μM ω-Agatoxin IVA (ATX). H–I Summary data of the effects of the N-type Ca2+ channel blocker, on apical versus basal neurons. Table 1 illustrates the summary data for the effects of Ca2+ channel blockers on whole-cell Ca2+ currents.