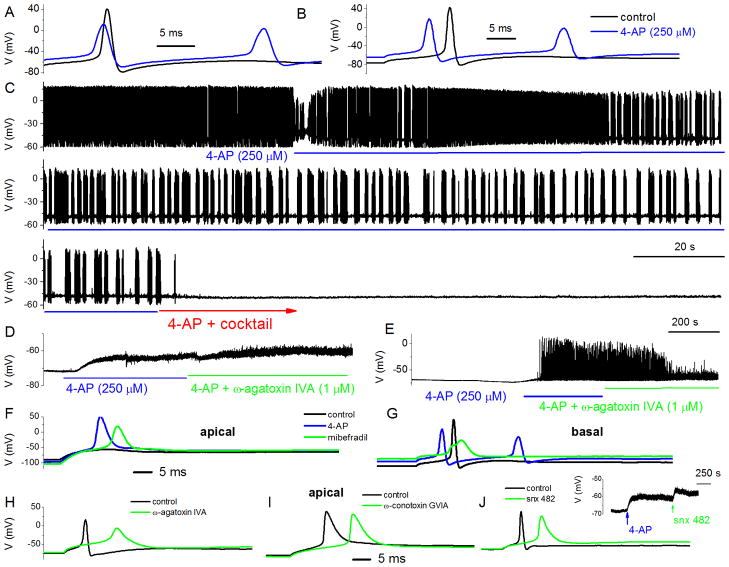
Figure 5. Effects of 4-AP and Ca2+ current blockers on membrane properties of adult SGNs.
To enhance and resolve the effects of Ca2+ current blockers on action potentials in SGNs, we used 4-AP (250 μM) to broaden the action potentials. A Evoked action potentials (0.2 nA current) recorded from a 3-month-old basal SGN, before and after application of bath solution containing 250 μM 4-AP. B Rebound action potentials following injection of negative current (−0.5 nA). C In spontaneously active SGNs, 4-AP altered the firing pattern. Upon application of bath solution containing 4-AP and a cocktail of Ca2+ current blockers (10 μM nimodipine for L-type, 1 μM ω-Agatoxin IVA (ATX) for P/Q-, 1 μM ω-Conotoxin MVIIA (CTX) for N-, 200 nM rSNX-482 for R-, and 5μM mibefradil for T-type currents), spontaneous activity was attenuated. D Besides alteration of the shape and firing patterns of action potentials, 250 μM 4-AP was sufficient to produce substantial depolarization of SGNs (rmp for control −65 ± 9 mV after application of 4-AP, −61 ± 7 mV (n = 8)). Blockade of P/Q-type Ca2+ currents with 1 μM ω-Agatoxin IVA resulted in small but consistent depolarization of the rmp (controls = −64 ± 8 mV after ω-Agatoxin = −57 ± 2 mV (n = 8)). E In six out of ten SGNs 4-AP-induced-depolarization triggered spontaneous activity. Suppression of P/Q-type Ca2+ currents reduced the spike amplitude and frequency (five out of six SGNs). F Adult apical SGNs was injected with −0.5 nA, and slight rebound depolarization followed (in black trace). Upon application of 250 μM 4-AP solution, injection of −0.5 nA sufficed to elicit rebound action potential (in red). Shown in green trace is the resulting action potential after application of bath solution containing 250 μM 4-AP and 5 μM mibefradil. G Similar but not identical data obtained from age-matched basal SGNs. H The resulting effects of blockade of P/Q-type current (control in black and after 4-AP and toxin in green traces) in apical SGNs. The 4-AP-mediated traces were omitted for clarity but see Table 2. I & J Changes in action potential properties following inhibition of N- and R- type Ca2+ currents, respectively. Shown in the inset is the effect of 4-AP and the R-type channel blocker on the rmp. Table 2 outlines the summary data from both apical and basal SGNs.