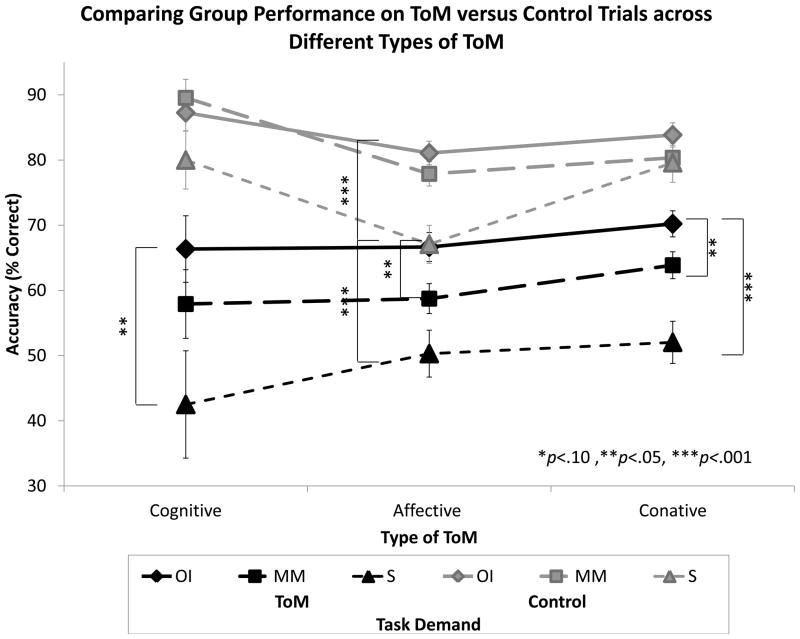
Figure 5. Accuracy by Type of ToM and Task Demand (ToM versus Control).
Within all three types of ToM, performance was significantly better on Control than on ToM conditions (p<.001 for each domain). Within Control conditions, performance was significantly better on Cognitive than either Affective (p<.001) or Conative (p=.044) ToM, and better on the Conative than the Affective domain (p<.001). Within ToM conditions, performance was similar on Cognitive and Affective domains (p=.427), but marginally better for Conative than either Cognitive (p=.071) or Affective (p=.075) ToM.