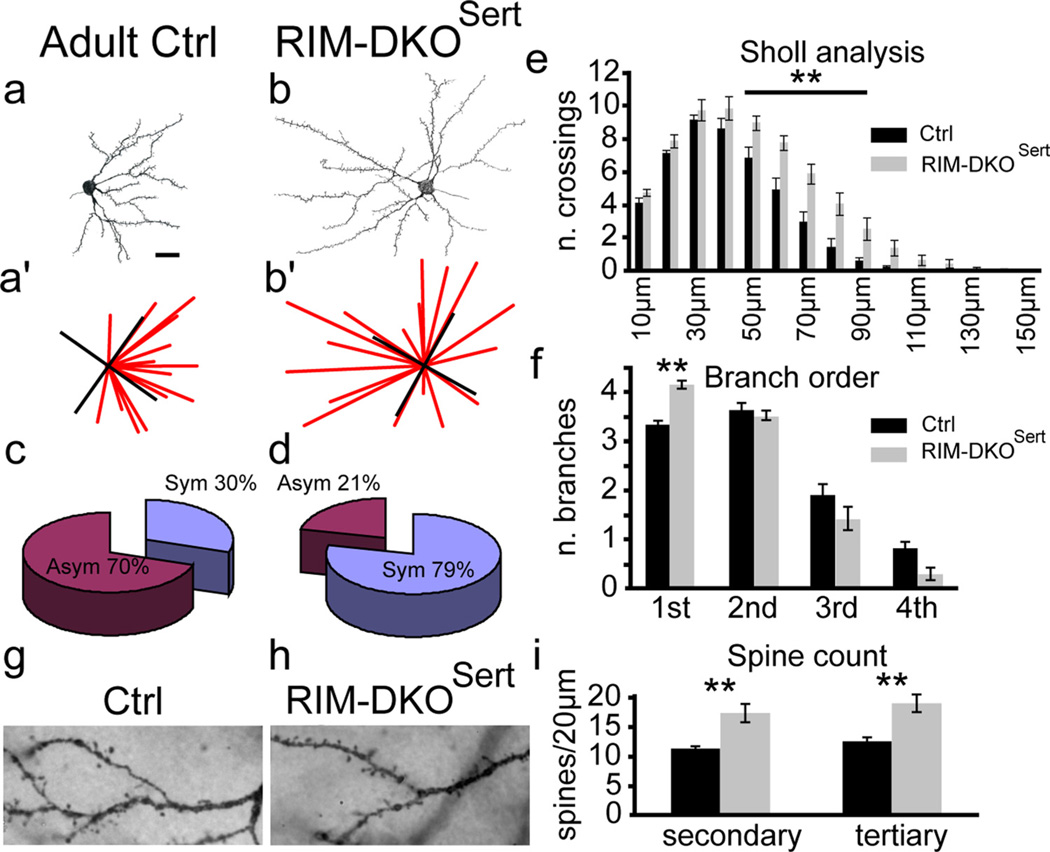
Figure 6.
Morphology of layer IV cortical neurons in RIM-DKOSert mice. a, b, Camera lucida drawings of Golgi-Cox-stained spiny stellate neurons in the barrel cortex. Typical layer IV neurons from control (a) and RIM-DKOSert (b) are illustrated. (a′, b′) to measure dendritic orientation, lines were drawn from the tip of each dendrite to the center of the cell soma; and the number of lines per quadrant was taken as an index of dendritic symmetry. c, d, The pie charts present the percentage of assymetric/symetric profiles for control (c) and RIM-DKOSert (d) mice. e, Sholl analysis: the histograms represent the mean number (+SEM) of dendrites crossing concentric rings drawn at 10 µm intervals from the cell soma. f, Histogram depicting the mean + SEM of first, second, third, and fourth order dendritic branches of spiny stellate neurons in control and DKOSert mice. g, h, micrographs of Golgi stained second and third order dendrites. Spines appear to be more numerous in the RIM-DKOSert neurons (h), than in controls (g). i, Histogram of the mean + SEM spine counts on 20-µm-long sections of second and third order dendrites of neurons from RIM-DKOSert and control brains. **p < 0.05. Scale bar, 20 µm.