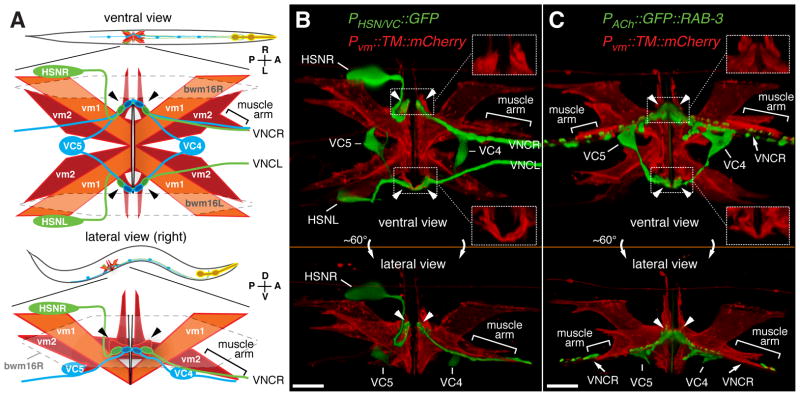
Figure 1. Anatomy of the egg-laying system.
(A) Cartoons showing ventral (top) or lateral (bottom) views of C. elegans and expanded views of the egg-laying system. HSN (green) and VC (blue) motor neurons as well as vm1 (orange) and vm2 (red) vulval muscles are shown. Six VC neurons send processes along the right ventral nerve cord (VNC). VC4 and VC5 have cell bodies close to the vulva and extend processes bilaterally to the vm2s. vm2 cells extend arms laterally onto which HSN and VC presynaptic termini form (arrowheads). vm2 cells on the right side also extend separate muscle arms (brackets) which receive additional synapses from the right ventral nerve cord. Gap junctions electrically connect vm cells, but anterior and posterior vm cells appear to be isolated from each other (solid black lines) but postsynaptic to the same neurons. The vulval muscles fill a gap between body wall muscle cells bwm16L/R (indicated with dashed line). Axes indicating Anterior, Posterior, Left, Right, Dorsal, and Ventral are shown here and in subsequent figures. Micrographs and schematics in this work are often right lateral views to allow visualization of the synapses between vm2 and the right ventral nerve cord.
(B) Presynaptic motor neurons interact with the vulval muscle at a large postsynaptic terminus. Transgenic worms expressed mCherry fused to a transmembrane domain (TM::mCherry) at the plasma membrane from a vulval-muscle specific promoter (Pvm) and expressed GFP from a second promoter strongly in the HSN and weakly in the VC4 and VC5 neurons. Arrowheads indicate presynaptic varicosities, and regions indicated with dotted boxes are magnified at right corners (150%) with only TM::mCherry labeling to reveal the vulval muscle postsynaptic termini onto which the HSN and VCs make synaptic contact. Bar, 10 μm.
(C) Same as (B) except that the GFP label is the presynaptic marker GFP::RAB-3 expressed in all cholinergic neurons. This marker fills out the VC4 and VC5 cell bodies and labels their presynaptic termini onto the vm2 lateral projections (arrowheads). It also produces punctate labeling of additional ventral nerve cord (VNC) synapses, and these may include the synapses made between VC neurons, by VCs onto vm2 muscle arms (brackets), and by other ventral nerve cord motor neurons onto vm1 cells (White, J.G. et al., 1986). Bar, 10 μm.