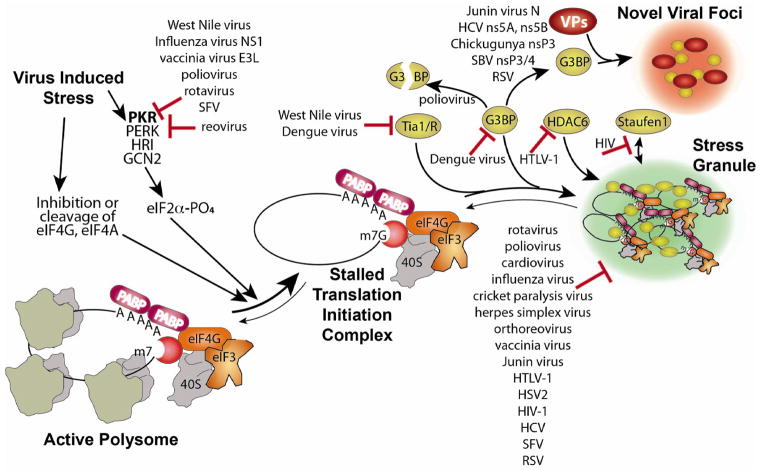
Figure 2.
P-body assembly and interference by viruses. P-bodies form via a complex series of events involving stripping of mRNPs of initiation factors and ribosome subunits, association with GW182, undergoing Pan2/3-mediated deadenylation, MT transport, and association of other RNA decay factors (e.g., Xrn1, Dcp1a, DDX6, GW182 and Lsm components of the exosome), and final concentration in P-bodies. Decapping and decay occurs both in and outside P-bodies. The order of association of factors with mRNPs in PBs is arbitrary. For HCV, novel viral foci containing P-body components also contain some SG components including G3BP.