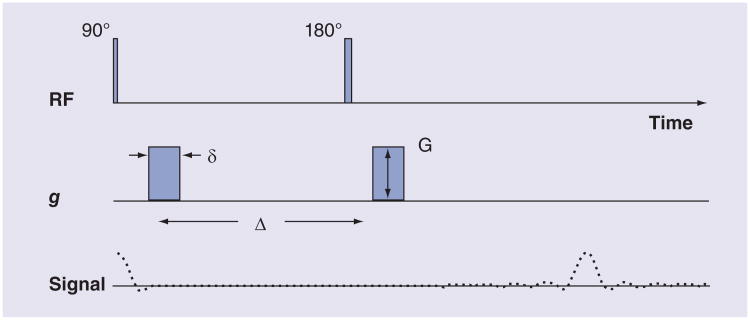
Figure 1. A diffusion-weighted imaging sequence.
Typical timing of events that occur with a diffusion-weighted imaging sequence. They include application of r.f. pulses, consisting of 90° and 180° (inversion) pulses, and gs. The sequence of signals generated is also shown. Not shown are the imaging gradients, which are required for the measurement of spatially localized magnetic resonance signals. The diffusion weighting or b-value is defined by δ, G and Δ.
δ: Diffusion gradient duration; Δ: Time between application of identical diffusion gradients; g: Diffusion gradient; G: Gradient amplitude; RF: Radiofrequency.