Figure 2.
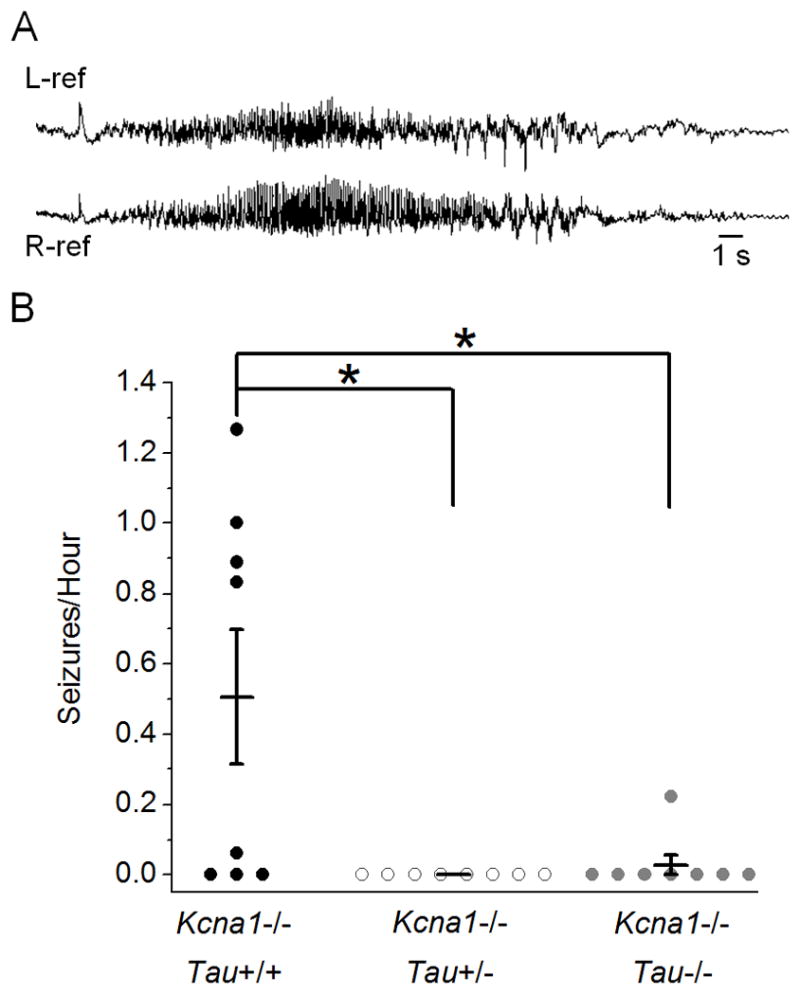
Tau reduction significantly decreases seizure frequency in Kcna1−/− mice. (A) Representative spontaneous cortical seizure recorded bilaterally in a Kcna1−/− mouse during chronic in vivo EEG monitoring. (B) Analysis of seizures/hour in double-mutant mice recorded for 9 or more hours. Both tau reduction and loss significantly decreased seizure frequency in Kcna1−/−Tau+/− (n=8) and Kcna1−/−Tau−/− (n=8) double mutants compared to Kcna1−/−Tau+/+ (n=8). Seizures were observed in 5/8 Kcna1−/−Tau+/+ mice, 0/8 Kcna1−/−Tau+/− mice, and only 1/8 Kcna1−/−Tau−/− mice. Total deletion of tau reduced the average seizure frequency by over 94%. * p<0.05; Kruskal-Wallis; error bars represent SEM.
