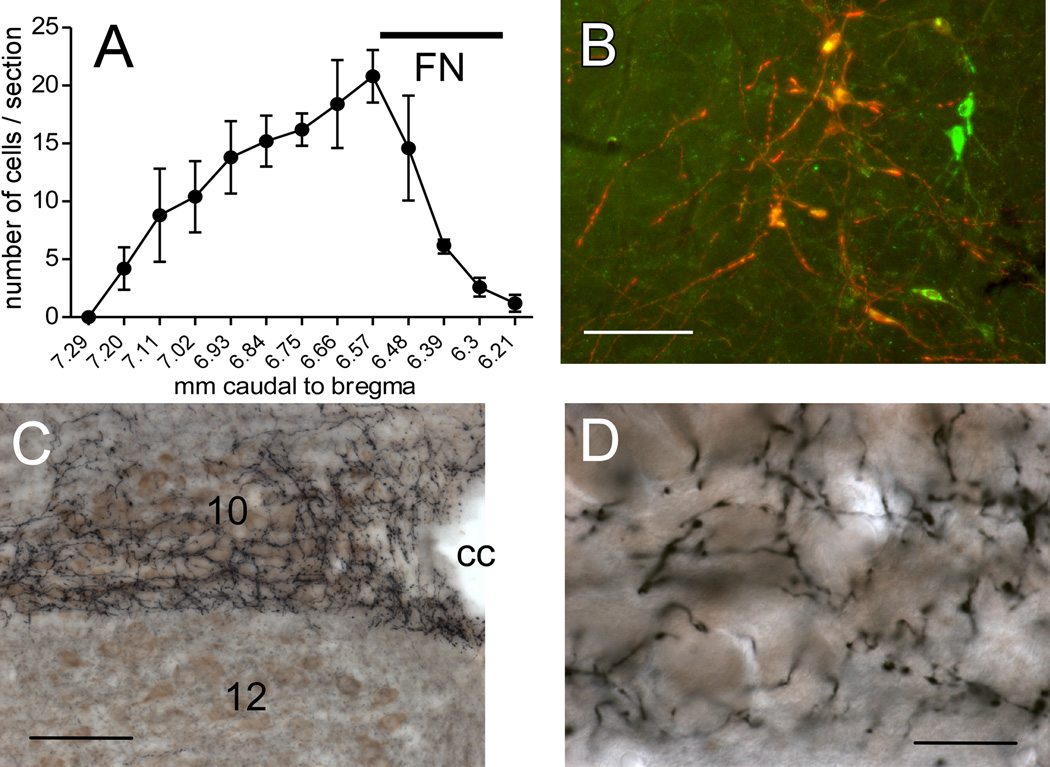
Figure 1. RVLM-Catecholaminergic (RVLM-CA) neurons innervate the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV) in DβH-Cre mice.
A, Rostrocaudal distribution of mCherry+TH-ir neurons (average of 5 cases). The ChR2-expressing neurons were confined to the RVLM. FN, caudal extent of the facial motor nucleus provided as reference. Dual-labeled neurons appear orange-yellow. Untransfected TH-ir neurons appear green. B, Photomicrograph of the RVLM one month after injection of AAV2-DIO-ChR2-mCherry into the same region in a DβH-Cre mice. mCherry immunoreactivity (red) is detectable exclusively in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-immunoreactive(ir) neurons (green). Scale, 100 µm. C, Photomicrograph showing the dense plexus of nerve terminals arising from mCherry-ir RVLM-CA neurons. ChR2-mCherry is visualized with the nickel-DAB method resulting in a black color. Choline acetyl-transferase (ChAT)-immunoreactivity is visualized with DAB resulting in a brown color. Note the dense terminal field in the DMV (10) that avoids the hypoglossal nucleus (12). cc, central canal. Scale, 200 µm. D, Higher power photomicrograph of the DMV innervation seen in C showing fibers and synaptic boutons arising from ChR2-expressing RVLM-CA neurons in close proximity of the DMV cholinergic neurons. Scale, 30 µm.