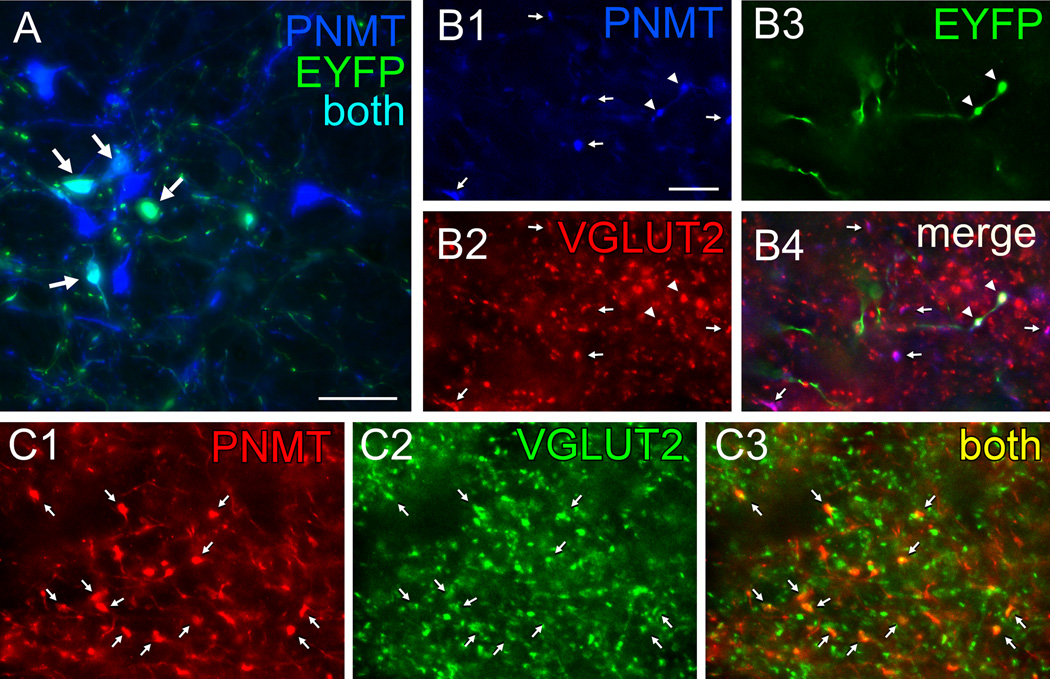
Figure 4. Axonal varicosities from C1 neurons in rat DMV contain PNMT and VGLUT2.
A, Photomicrograph showing that injection of AAV2-DIO-EYFP into the RVLM drives expression of EYFP in C1 (PNMT-ir) neurons in TH-Cre rats. EYFP immunoreactivity is in green and phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase (PNMT)-ir is in blue. Double labeled neurons appear aqua (arrows). Scale, 50 µm. B,Virtually all adrenergic varicosities (PNMT-ir, blue) within the DMV (B1, denoted by arrows or arrowheads) are also glutamatergic (VGLUT2-ir, red) (B2). The EYFP terminals (green) (B3, arrowheads) originating from C1 RVLM neurons are both adrenergic (red) and glutamatergic (green). B4, Merge of B1–B3. Triple labeled terminals (arrowheads) appear white. Double-label terminals (PNMT + VGLUT2) appear purple (arrows) when the colors are merged. C, Adrenergic terminals in DMV are also glutamatergic in naïve TH-Cre rats (no AAV2 injection). Adrenergic nerve terminals (PNMT-ir, red) located in DMV (C1) are also glutamatergic (VGLUT2-ir, green) (C2), arrows. These terminals appear yellow when the colors are merged in C3 (arrows). Note that practically all the PNMT-ir terminals are also VGLUT2-ir similar to the virus-injected rat shown in B. Scale in B1, 10 µm applies to B–C.