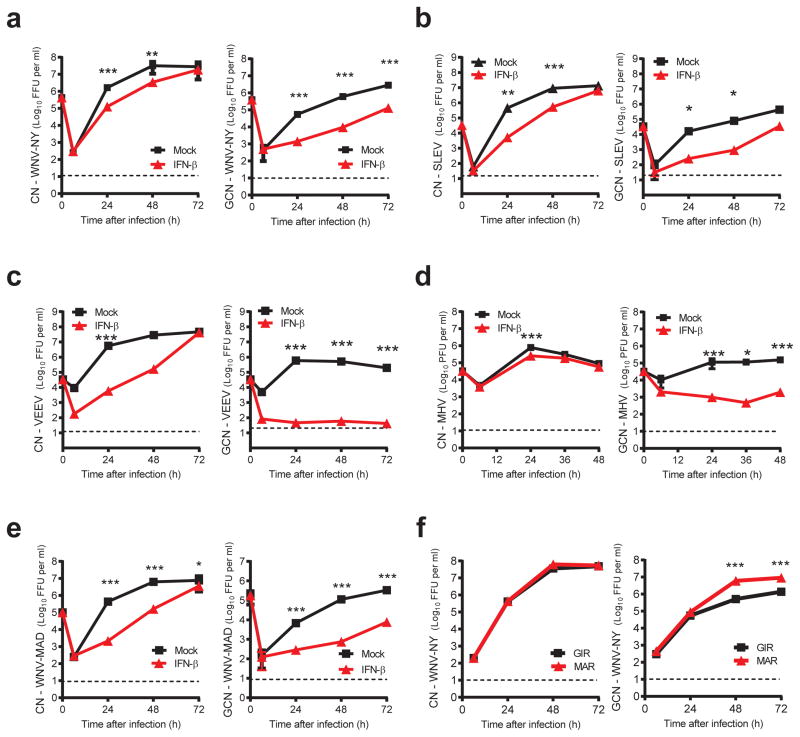
Figure 1. GCN are less susceptible to virus infection and more sensitive to the antiviral effects of IFN-β than CN.
Infection of (a) WNV-NY, (b) SLEV, (c) VEEV, (d) MHV, and (e) WNV-MAD in primary neurons. Primary CN and GCN generated from wild-type mice were pre-treated with medium (Mock) or IFN-β (100 IU/ml), infected at an MOI of 0.1 (WNV-NY and WNV-MAD) or 0.01 (VEEV, SLEV, and MHV), and virus production was evaluated at the indicated time points. (f) GCN and CN were treated with 20 μg/ml of MAR1-5A3 (MAR) anti-Ifnar MAb or an isotype control MAb (GIR-208 (GIR)) and viral replication was monitored. Results are the average of three independent experiments performed in triplicate and asterisks (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001) indicate differences that are statistically significant by an unpaired t test. Error bars indicate standard deviations (SD), and dashed lines indicate the limit of sensitivity of the assay.