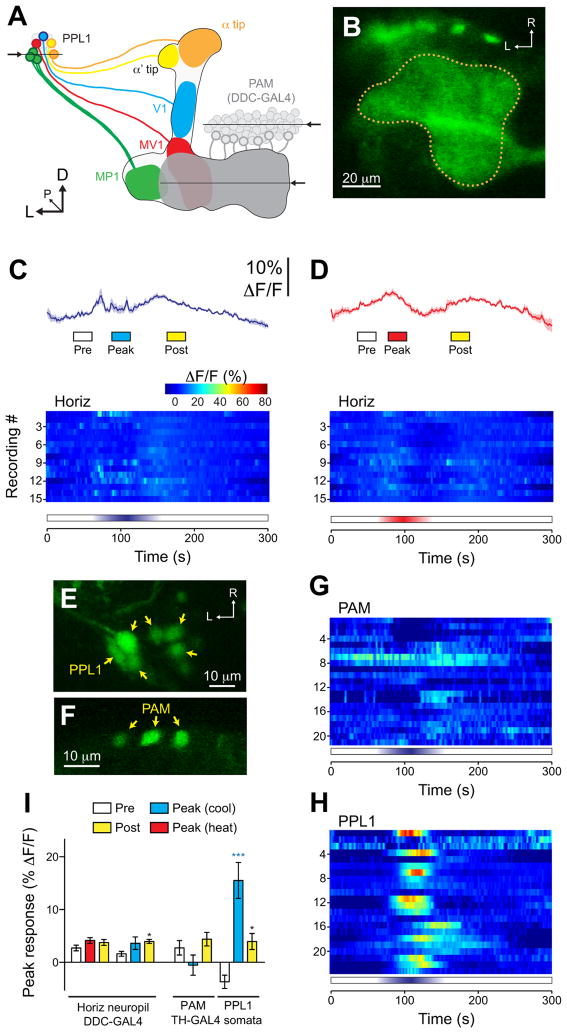
Figure 6.
Responses to cooling were specific to a subset of PPL1 dopaminergic neurons. A. Illustration of the dopaminergic neurons from the PPL1 and PAM clusters that innervate the mushroom body vertical and horizontal lobes, respectively. The mushroom body lobes are outlined, and each subset of dopaminergic neurons is illustrated in a different color. Arrows and horizontal lines indicate the planes of optical sections for the imaging experiments. B. Confocal image of GCaMP expressed in the PAM dopaminergic neurons innervating the horizontal mushroom body lobes, driven by Ddc-GAL4. The dotted line indicates the outline of the PAM neuropil innervating the mushroom body. C. Responses of the PAM neuropil to cooling. Mean (dark lines) ± S.E.M (light surrounds) are shown in the top panel, with heat maps below. D. Responses of the PAM neuropil to heating. The layout is the same as panel C. E. GCaMP expressed in the somata of PPL1 neurons with the TH-GAL4 driver. F. GCaMP expressed in scattered somata of PAM neurons with by the TH-GAL4 driver. G. Heat map showing the responses of individual PAM somata to cooling. H. Heat map showing the responses of individual PPL1 somata to cooling. I. Peak response magnitudes during three time windows (Pre, Peak, and Post; see bottom of panels C and D) across neuropil of PAM neurons innervating the horizontal mushroom body lobes (left side) and the somata of PPL1 and PAM neurons (right). *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 (Bonferroni).