Figure 6. Combined condition responses are well approximated by linear weighted summation.
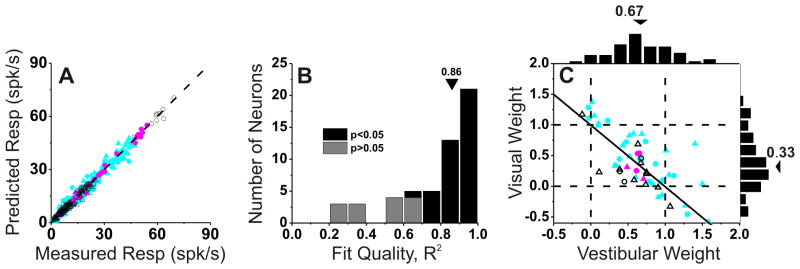
(A) Predicted responses from weighted linear summation are strongly correlated with measured responses under the combined condition (R=0.99, p≪0.001). Each symbol represents the response of one neuron at one heading angle (after spontaneous activity is subtracted). Cyan, red and black symbols are used for congruent (n=36), opposite (n=5) and intermediate (n=15) neurons, respectively. (B) Distribution of correlation coefficients from the linear regression fits. Three cases with negative (but not significant) R2 values are not shown. (C) Visual and vestibular weights derived from the best fit of the linear weighted sum model for each neuron with significant R2 values (black bars in B). Arrowheads illustrate mean values. Solid lines show Speakman rank correlation. Circles, monkey U; triangles, monkey C.
